Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
VISHODHANAM: E-Waste Handling Web Application
Authors: Manoj Damahe, Mrunali Jambhulkar, Prathmesh Suhagpure, Manoj Mamadge, Aashutosh Gawande, Prof. Mohammad Sajid
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2023.56366
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
VISHODHANAM E-waste Handling Web Application is an innovative online platform designed to handle the critical issues of electronic trash (e-waste) management. This online application provides a user-friendly interface adapted to the demands of consumers, companies, and recycling organizations, therefore expediting the e-waste disposal and recycling process. As electronic gadgets grow increasingly ingrained in our daily lives, the significance of appropriate e-waste management cannot be stressed. VISHODHANAM aspires to give a long-term solution to the rising problem of e-waste by not only simplifying the disposal process but also instilling a feeling of responsibility and understanding about the environmental effects of e-waste. VISHODHANAM is prepared to make a substantial contribution to the ongoing struggle to manage e-waste effectively. This study paper delves into the application\'s features, design, and possible influence on increasing environmental awareness and supporting responsible e-waste disposal and recycling.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
In today's world, we’re surrounded by electronic gadgets, which make our lives easier and more connected. This convenience, however, comes at a cost: electronic waste, or e-waste, is rapidly piling up. To address this issue, we developed the "VISHODHANAM: E-Waste Handling Web Application." It is an online tool that assists individuals and businesses in properly disposing of e-waste. Whether you have an old smartphone, a broken laptop, or outdated electronics, VISHODHANAM makes it simple to recycle them. In this paper, we'll look at how this web app works, how it benefits the environment, and how it encourages everyone to be more environmentally conscious in their e-waste management.
We're not just making e-waste management easier with VISHODHANAM; we're also raising awareness about the importance of responsible disposal. Our investigation focuses on the app's features and their impact on promoting environmentally friendly practices. We'll discuss how technology, sustainability, and public awareness intersect with e-waste. In the following sections, we'll review the technical details, methods we used, and real-world implications of VISHODHANAM, shedding light on its contribution to a greener, more sustainable future.

A. Global Quantity of Electronic Waste
Electronic waste, also known as e-waste, refers to discarded electronic devices with a battery or plug that are no longer wanted, functional, or obsolete. Lamps, small IT and telecom equipment, screens and monitors, temperature exchange equipment, large equipment, and small equipment are the six major categories of e-waste. Small equipment, such as microwaves, hoover cleaners, and kettles, accounts for the lion's share of e-waste produced by weight. Every year, more than 50 million metric tonnes of e-waste are generated globally, with an average of seven kilograms of e-waste per capita.
B. Recycling and electronic waste in India
According to data from the Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change, India recycled only 32.9 percent of the e-waste generated in 2021-2022. While the figure is higher than in previous years, it still shows that a staggering 10,74,024 tonnes (67%) of e-waste went unprocessed.
Unprocessed e-waste is hazardous to human health and the environment because it contains toxic substances such as lead, cadmium, mercury, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), etched chemicals, arsenic, and asbestos, which can be dangerous if not disposed of properly. These toxic chemicals may leach into the soil and pose an environmental risk if not separated from other solid waste that ends up in landfills.
C. Environmental Affect
- In developing countries, approaches to dismantling and removing digital waste have some environmental consequences.
- When e-waste is heated, poisonous chemical compounds are released into the atmosphere.
- When digital waste is disposed of in landfills, its toxic substances seep into groundwater, affecting both land and sea animals.
- Liquid and atmospheric releases end up in bodies of water, groundwater, soil, and air, and thus in land and sea animals - both domesticated and wild.
- One of the most significant environmental consequences of E-waste is pollution.
II. LITERATURE SURVEY
- "A Comprehensive Review on E-Waste Management Strategies and Prediction Methods: A Saudi Arabia Perspective"
This 2023 study examines how Saudi Arabia manages e-waste. It discusses strategies and methods for managing and reducing e-waste. The study demonstrates the importance of predicting e-waste to use resources wisely.
2. "Growing e-waste management risk awareness points towards new recycling scenarios: The view of the Big Four's youngest consultants"
This 2021 study focuses on how young consultants from large firms perceive the risks associated with e-waste management. It implies that we should be more aware of the challenges and consider new ways to recycle e-waste.
3. "IoT-Based Smart E-Waste Management System"
This research presents an "IoT-Based Smart E-Waste Management System." It involves using the Internet of Things (IoT) to track e-waste in real time. This can assist us in making better decisions about how to manage e-waste.
4. "SMART GARBAGE COLLECTING BIN FOR MUNICIPAL SOLID WASTE"
This study discusses a "smart" bin for collecting regular waste rather than just e-waste. It demonstrates how smart technology can improve waste collection efficiency.
III. PROBLEM STATEMENT
Electronic waste, e-scrap, and end-of-life electronics are all terms used to describe used electronics that have reached the end of their useful life and are discarded, donated, or given to a recycler. The United Nations defines e-waste as any discarded product with a battery or plug that contains toxic and hazardous substances such as mercury, which can endanger human and environmental health.
According to the UN, in 2021, each person on the planet will generate 7.6 kg of e-waste, resulting in a massive 57.4 million tonnes being generated globally. Only 17.4% of this electronic waste, which contains a mix of hazardous substances and valuable materials, will be properly collected, treated, and recycled. Many initiatives are being launched to address this growing concern, but none of them will be fully effective unless consumers play an active role and are properly educated.
- Inefficient E-Waste Management: Current e-waste management practices frequently lack efficiency and user-friendliness, resulting in haphazard disposal, which contributes to environmental pollution and resource waste.
- Lack of Awareness: A general lack of awareness about the environmental implications of e-waste exists. As a result, electronic devices are discarded carelessly, either in landfills or through incineration, exacerbating pollution and resource depletion.
- Data Security Risks: Improper e-waste disposal raises serious data security concerns. Electronic devices frequently contain sensitive data that must be securely wiped out before disposal to prevent data breaches, protect privacy, and protect intellectual property.
- Health and Environmental Consequences: Improperly managed e-waste poses environmental and health risks. The release of hazardous materials into the environment can harm both human health and the environment.
- Recycling Difficulties: The presence of complex and non-recyclable components in some electronic devices complicates recycling, impeding resource recovery and long-term e-waste management.
IV. PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
A. Needs Assessment
- Determine the specific needs and requirements of users, such as consumers, businesses, and recycling organizations.
- Conduct surveys, interviews, and research to better understand user preferences and e-waste handling challenges.
B. Technology Selection
- Select the appropriate technology stack for the development of the web application.
- For efficient performance and convenience, consider user-friendly and scalable technologies.
C. User Interface (UI) Design
- Create an intuitive and user-friendly interface for the web application.
- Ascertain that the design meets the needs of various user groups and promotes easy navigation.
D. Awareness and Education
- Create educational materials and resources within the app to raise awareness about the environmental impact of e-waste and proper disposal methods.
- To encourage responsible e-waste management, including user-friendly guides and tips.
E. Deployment and Scaling
- Deploy the application to a larger audience by making it more widely available.
- Plan for scalability to accommodate growing user and data volumes.
F. Continuous Improvement:
- Update and improve the application regularly based on user feedback and changing e-waste management requirements.
- Keep up with technological advances and environmental regulations.
G. Campaigns for User Engagement and Awareness:
- Implement user engagement strategies and awareness campaigns to promote responsible e-waste disposal.
- For a greater impact, collaborate with environmental organizations and government agencies.
V. PROPOSED SOLUTION
The "VISHODHANAM - E-Waste Handling Web Application" was created to be a comprehensive and user-friendly platform that addresses the challenges associated with electronic waste (e-waste) management. It aims to promote responsible e-waste disposal, raise environmental awareness, and make recycling more efficient.
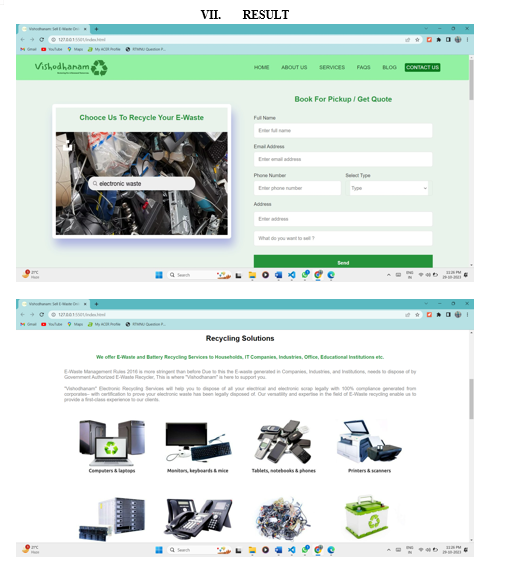
- E-Waste Collection Requests: This feature enables users to easily submit e-waste collection requests. Users can specify the type and number of electronic items to be disposed of. This feature simplifies the process of scheduling e-waste pickups, ensuring that users can dispose of their electronic devices easily and responsibly.
- Raising Environmental Awareness: "VISHODHANAM" understands the critical importance of raising awareness about the environmental impact of e-waste. The app includes a variety of materials and visualizations that educate users on the dangers of improper e-waste disposal. The app provides users with knowledge by delivering easily digestible and informative content, motivating them to take action towards responsible recycling.
- Decomposition Awareness: Recognizing the difficulties of e-waste decomposition is essential for responsible disposal. The application is crucial in informing users about these challenges. "VISHODHANAM" encourages users to make informed decisions about the end-of-life management of their electronic devices by emphasizing the environmental impact of e-waste decomposition and the importance of responsible handling.

VI. SOFTWARE USED
The creation of "VISHODHANAM - E-Waste Handling Web Application" requires the use of many software tools and technologies to create an efficient and user-friendly platform. The following software was used in the development process:
A. Programming Languages
- Front-end Development: HTML, CSS, Bootstrap, JavaScript
- Back-end Development: PHP, XAMPP
- Database Management: MySQL
B. Database Management:
MySQL: Database management software for storing user information, e-waste pickup requests, and other relevant data.
C. Version Control:
Tools for collaborative development, tracking changes, and managing the codebase, such as Git and GitHub.
D. Integrated Development Environment (IDE):
Visual Studio Code is a streamlined code editor with support for development operations like debugging, task running, and version control. It aims to provide just the tools a developer needs for a quick code-build-debug cycle and leaves more complex workflows to fuller featured IDEs, such as Visual Studio IDE.
E. User Interface (UI) Design Software:
Figma: Figma is a cloud-based design tool that is similar to Sketch in functionality and features, but with big differences that make Figma better for team collaboration. We can use Figma for UI/UX designs, graphics design, wireframing, diagramming, brainstorming, and remote designs.
VIII. ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Prof. Mohammad Sajid deserves our heartfelt gratitude for his insightful feedback and guidance in shaping our project. Dr. Shrikant Zade, Head of the Department of Computer Science & Engineering, is also acknowledged for his unwavering support. We appreciate the resources provided by our Principal, Dr. Amol Deshmukh, and the Computer Science & Engineering department's dedicated teaching and support staff. We would like to express our gratitude to the library staff and all contributors to this project, as well as our parents, for their unwavering support.
Conclusion
Ultimately, \"VISHODHANAM - E-Waste Handling Web Application\" provides a complete and user-friendly solution to the complex challenges of electronic waste (e-waste) management. It enables users to dispose of e-waste responsibly, educates them about its environmental impact, ensures data security, and advocates for long-term decomposition. This innovative application is the result of a collaborative effort and represents an important step towards a more responsible, aware, and environmentally conscious approach to e-waste management.
References
[1] Madkhali, H., Duraib, S., Nguyen, L., Prasad, M., Sharma, M., & Joshi, S. (2023). A Comprehensive Review on E-Waste Management Strategies and Prediction Methods: A Saudi Arabia Perspective. 163–179. [2] Appolloni, A., D’Adamo, I., Gastaldi, M., Santibanez-Gonzalez, E. D. R., & Settembre-Blundo, D. (2021). Growing e-waste management risk awareness points towards new recycling scenarios: The view of the Big Four’s youngest consultants. Environmental Technology and Innovation. [3] Pallavi Bansod1, Sonali Shende, Rajat Gajbhiye, Sujata Sardar, Aslam Ghodke, Prof. S.S. Sawwashere, IoT Based Smart E-Waste Management System. [4] Arunkumar, Bhanu Priya, Prof. R. Santhosh Kumar, \"SMART GARBAGE COLLECTING BIN FOR MUNICIPAL SOLID WASTE\", IJMTES | International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Science, Volume: 03 Issue: 03 201 [5] Prof. Mayur Tiwari, Aboli Deshmukh, Kshitija Boke, Netra Deshmukh, Ashwini Dhurve, \"SMART WASTE MONITORING SYSTEM\", Prof. Dept. of Electronics and Telecommunication, Prof. Ram Meghe Institute of Technology and Research, Badnera, Amravati, Maharashtra, India, International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), Volume: 06 Issue: 04 Apr 2019e-ISSN: 2395-0056, ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal. [6] S. Sanjay Kumar, Ch. Rajendra Prasad,\"Garbage Monitoring System using Arduino\", International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD) ISSN: 2456-6470, Volume-1, Issue-6, DOI:10.31142/ijtsrd4602. [7] M. Khurrum S. Bhutta, Adnan Omar, and Xiaozhe Yang” Electronic waste: A Growing Concern in Todat’s Environment” Economic Research International, 2011 (), 1-8, DOI:10.1155/2011/474230. [8] P. Ramchandar Rao, “Garbage Monitoring System using Arduino”, International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD), Volume1, Issue-6, Sep-Oct:2017, ISSN No:2456-6470
Copyright
Copyright © 2023 Manoj Damahe, Mrunali Jambhulkar, Prathmesh Suhagpure, Manoj Mamadge, Aashutosh Gawande, Prof. Mohammad Sajid. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET56366
Publish Date : 2023-10-29
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

