Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- References
- Copyright
What Comprises of Job Satisfaction in Modern Employees? (IT Industry)
Authors: Naveen R, Dr. Nalini Sunil
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.60022
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
In the rapidly changing modern workplace, it is extremely important for companies looking to recruit, retain, and inspire people to have a thorough awareness of the elements influencing modern workers\\\' job satisfaction, especially in the IT sector. In an effort to better understand the complexities of modern workplaces, this research study examines the intricate interactions among work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction. Research gaps were found using an extensive evaluation of the literature, which prompted the development of research hypotheses. Data was gathered through secondary data analysis and questionnaire surveys using a quantitative research technique. The results showed a strong relationship between job satisfaction and staff engagement, highlighting the value of encouraging employee involvement to raise overall job satisfaction. Even though there was less of a correlation, there was still a favourable association between work-life balance and job satisfaction, demonstrating the significance of encouraging a good balance between work and personal duties. Theoretical implications emphasised the importance of work-life balance and employee engagement in fostering both organisational success and employee well-being, and they highlighted the role that job satisfaction plays in organisational well-being. The insights gained from managerial implications included customised employee engagement plans, adaptable work schedules, resource allocation for employee assistance, and the encouragement of inclusivity and diversity in the workplace. Despite many drawbacks, including possible self-reporting biases and the cross-sectional design, this study offers insightful information about the variables affecting job satisfaction in contemporary settings. Organisations can establish work cultures that promote employee satisfaction, productivity, and long-term success by placing a high priority on employee engagement, promoting work-life balance, and valuing diversity and inclusion.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE
A. Introduction
In the present dynamic and quickly developing work scene, understanding the variables that add to work fulfilment among current representatives has become progressively essential for associations endeavouring to draw in, hold, and persuade their labour force. Work fulfilment, a complex build including different parts of a singular's insight and experience inside the work environment, fills in as a critical sign of hierarchical well-being and representative prosperity. In this unique circumstance, investigating the complicated exchange between work fulfilment and its determinants, especially representative commitment and balance between serious and fun activities, arises as a relevant area of examination pointed toward disentangling the intricacies of contemporary workplaces.
The idea of occupation fulfilment, established in hierarchical brain research and human asset board writing, mirrors representatives' general satisfaction, satisfaction, and bliss with their positions and business-related encounters. It includes a wide cluster of variables, going from natural inspirations, for example, significant work and independence to extraneous elements like remuneration, advantages, and workplace. As associations explore the difficulties presented by globalization, innovative progressions, and changing labour force socioeconomics, understanding the developing idea of occupation fulfilment becomes basic for encouraging a positive hierarchical culture and upgrading representative execution and maintenance.
Representative commitment, perceived as a critical driver of hierarchical achievement, relates to the close-to-home, mental, and social association workers have with their work jobs, partners, and the association in general. It envelops perspectives like work association, excitement, responsibility, and optional exertion, all of which fundamentally impact work fulfilment levels. The research proposes that drew-in representatives are bound to encounter more elevated levels of occupation fulfilment, as they determine a feeling of direction, satisfaction, and arrangement with hierarchical objectives from their work encounters.
Essentially, the balance between serious and fun activities has arisen as a basic determinant of occupation fulfilment, especially in a time described by mechanical networks, globalization, and changing cultural standards. The balance between serious and fun activities alludes to the harmony people try to accomplish between their expert obligations and individual responsibilities, including family, social, and recreation exercises. Representatives who see a good arrangement among work and individual life are bound to encounter decreased pressure, upgraded prosperity, and more prominent work fulfilment, prompting further developed execution and hierarchical results.
Against this background, this exploration plans to dig into the mind-boggling elements of occupation fulfilment among current representatives, with a particular spotlight on the job of worker commitment and balance between fun and serious activities as essential determinants. By analyzing the connection between these factors, this study tries to clarify the elements that add to work fulfilment in contemporary work settings, offering experiences that can illuminate hierarchical approaches, practices, and mediations pointed toward upgrading representative prosperity and authoritative adequacy. Through a complete examination of the transaction between representative commitment, the balance between serious and fun activities, and occupation fulfilment, this exploration tries to add to the more extensive comprehension of labour force elements and hierarchical conduct in the cutting-edge working environment scene.
B. Rationale For The Study And Motivation
- Organizational Performance: Since job satisfaction is correlated with both productivity and profitability inside a company, it is imperative to understand it. More dedication and effort are typically shown by engaged workers, which improves productivity and creativity.
- Employee Retention: Since job satisfaction has an impact on retention, it's critical to pinpoint the elements that influence satisfaction. With this information, organizations may put initiatives in place that lower attrition and increase talent retention.
- Employee Well-Being: Both physical and mental health of employees are impacted by job satisfaction. By addressing satisfaction, employers can promote a healthier workforce by reducing absenteeism and burnout.
- Talent Development: Contented workers are more inclined to take advantage of possibilities for learning and growth. Succession planning and career advancement can be aided by talent development programs that are informed by satisfaction.
- Key Considerations:
- Social Impact: Improving work happiness can have a positive impact on social cohesion and economic prosperity.
- Intellectual curiosity is satiated by conducting studies in this discipline, which enables scholars to make contributions to the domains of organizational psychology and human resource management.
- Practical Application: The goal of the research is to give organizations practical advice on how to improve engagement, foster work-life balance, and build supportive work environments.
6. Motivations:
- Interest in Human Behavior: A strong desire to comprehend organizational dynamics and human behavior drives researchers.
- Desire for Positive Change: The research intends to benefit both individuals and companies by promoting healthier and more equal workplaces.
- Application of Insights: The research aims to promote constructive modifications in organizational practices and policies by producing evidence-based suggestions.
C. Statement Of The Research Problem
The present study challenge centres on comprehending the complex interplay among work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction in contemporary organizational environments. Even while these elements are acknowledged to be important, there is still a lack of research thoroughly examining how they interact and impact one another in the modern workplace. The following important questions are addressed in the problem statement:
- What Makes a Job-Satisfied Employee? The issue statement's first section explores the various components that modern employees find satisfying in their jobs. This means identifying the precise elements that influence workers' general job happiness, from extrinsic incentives to intrinsic motivators.
- Impact of Employee Engagement: The purpose of the study is to clarify how employee engagement influences job satisfaction as an independent variable. Determining the impact of employee engagement on overall job satisfaction levels requires an understanding of how engaged workers view their work and how it aligns with corporate goals.
- Dynamics of Work-Life Balance: The study problem highlights the importance of work-life balance, with a particular emphasis on how employees' job happiness is influenced by their capacity to balance personal and professional obligations. Investigating the complexities of work-life balance and how it interacts with job satisfaction yields important information on the productivity and well-being of today's workforce.
- Interrelationships between Variables: The goal of the study challenge is to understand the intricate linkages that exist between work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction. Through a detailed analysis of these variables, the study seeks to identify any subtle patterns or dependencies that could exist, providing a more thorough knowledge of their combined influence on organizational outcomes and employee happiness.
D. Review Of Literature
Hu, N., Poon, S., Zhong, J., and Wan, Y. (2004) directed an experimental examination concerning the work fulfilment of Data Innovation (IT) experts, zeroing in on those in information warehousing and business knowledge areas. Through Staggered request calculated relapse examination, the review inspected how non-financial variables, including position plan and client foundation, impact work fulfilment while controlling for monetary elements. The discoveries uncovered that IT experts show higher work fulfilment when their jobs line up with vocational assumptions and company techniques, and when they have suggesting and dynamic power. The concentrate likewise featured a pattern towards IT experts looking for administrative and key dynamic jobs, demonstrating a change in industry inclinations. By and large, the examination highlights the significance of thinking about non-financial variables in grasping position fulfilment among current IT experts and proposes the requirement for associations to adjust their ways to deal with draw-in and hold ability successfully.
Kamalanabhan, T. J., Sai, L. P., and Mayuri, D. (2009) distributed in Mental Reports examines the connection between representative commitment and occupation fulfilment inside the data innovation (IT) industry. Perceiving the meaning of representative commitment for efficiency and execution, the analysts created measures to survey worker commitment and occupation fulfilment explicitly customized to the IT setting. Through an example of 159 IT experts, the review tracked down a critical and positive connection between representative commitment and occupation fulfilment, even after controlling for different elements. The specialists highlighted the significance of this relationship with regard to the product administration industry, which appears challenges connected with weakening and occupation fulfilment. Drawing on past exploration, the review investigated the complex idea of representative commitment, underscoring its part in encouraging a positive, satisfying business-related state portrayed by force, devotion, and retention. Also, the build of occupation fulfilment, broadly explored in a hierarchical way of behaving, envelops attitudinal, full of feeling, and dispositional angles. The review features the requirement for additional exploration on work fulfilment inside the Indian IT industry, given its quick development and difficulties in holding gifted representatives. By creating measures customized to the Indian setting, the review intends to give significant experiences to bosses and supervisors to upgrade worker commitment and occupation fulfilment inside IT associations. This examination adds to figuring out the elements of representative commitment and its suggestions for work fulfilment, especially inside the setting of the expanding IT industry in India.
Kanwar, Y. P. S., Singh, A. K., & Kodwani, A. D. (2009) in their study, "Work—Life Balance and Burnout as Predictors of Job Satisfaction in the IT-ITES Industry" examine the impact of burnout and work-life balance on job satisfaction in the IT and IT Enabled Services (ITES) sectors. The study intends to shed light on factors contributing to decreased employee turnover, higher engagement, and increased productivity in light of the importance of job satisfaction for organisational success. The elements of meaninglessness, demotivation, and tiredness are used to study burnout. The results indicate a positive correlation between job satisfaction and work-life balance, but demotivation, weariness, and meaninglessness—dimensions of burnout—show negative correlations with job satisfaction. Notably, work-life balance is found to be a major factor in determining job satisfaction in both the IT and ITES industries, with a greater effect in the ITES group. The study also shows disparities in job satisfaction by gender, with male respondents reporting higher job satisfaction than female respondents. It's interesting to note that, in comparison to the ITES group, the IT group exhibits lower levels of job satisfaction and work-life balance but higher levels of burnout dimensions. The study ends with a discussion of the implications of raising employee happiness and recommendations for more research in this area.
Hussin's doctoral exposition (2011) examines the connection between work fulfilment and occupation execution among representatives inside the Tradewinds Gathering of Organizations. The review plans to survey the degrees of occupation fulfilment and occupation execution and distinguish how different parts of occupation fulfilment, including pay, advancement, actual work, management, and colleagues, impact work execution. Led among 115 respondents in the Klang Valley area, the review uses the entire populace strategy.
The discoveries uncover a positive connection between work fulfilment parts like advancement, the actual work, management, and collaborators, with work execution. In any case, there was no critical relationship secured between pay and position execution. Moreover, the review features a huge distinction in work execution in light of the representative situation inside the association. Generally speaking, the exploration recommends that work fulfilment aspects assume an essential part in upgrading position execution, with pay, advancement, the idea of work, oversight, and associations with collaborators adding to an eminent 17.8% expansion in hierarchical work execution. This study extends important bits of knowledge into the interaction between employment opportunity fulfilment and occupation execution inside the setting of the Tradewinds Gathering of Organizations, revealing insight into factors that might work on authoritative execution and representative results.
Kassim, E. S., Ali, S. A. M., Jalaini, S. F. A. K., Said, N. A., Ab Latiff, D. S., & Salleh, F. (2013) in their study, "Work-life balance and job satisfaction: How relevant are they?" examine the significance of work-life balance and its effect on job satisfaction among management personnel in healthcare organisations. Although obtaining job satisfaction is a critical component of employee well-being, doing so can be difficult, thus businesses must take a more humanistic stance towards their employees. The study intends to investigate work-life balance's role as an antecedent to job satisfaction, given its importance in promoting job satisfaction. Participants in a poll with 205 management staff members were asked to rank comments about motivation, social support, and workplace culture. According to hypothesis testing, motivation, social support, and workplace culture have a big impact on how employees feel about their jobs. The research highlights the significance of organisations reassessing their policies, procedures, and standard operating guidelines in order to facilitate a harmonious coexistence of workers' personal and professional lives. In order to produce more thorough results, the authors further recommend enlarging the population group and extending the scope of work-life balance in future studies. Overall, the survey emphasises how important work-life balance is for improving job satisfaction and how important it is for businesses to give employee well-being initiatives top priority, both within and outside the workplace.
Melián-González, Bulchand-Gidumal, and Gonzalez Lopez-Valcarcel (2015) investigate the connection between worker fulfilment and firm monetary execution, expecting to give new bits of knowledge into what representative mentalities mean for authoritative results. The review researches three firm-level execution markers: return over resources, working edge, and income per representative, comparable to worker fulfilment. Information from 475 firms, acquired from two autonomous sources at various times, were broken down, making this study one of the biggest to analyze the connection between execution and worker fulfilment at the firm level. The discoveries propose that general fulfilment and explicit features like fulfilment with senior initiative, pay, and work/life balance essentially impact firm execution. In any case, the review recognizes impediments, like the dependence on evaluations from both current and previous representatives, with obscure individual qualities, as well as potential predispositions innate in web-based studies. By and by, the reasonable ramifications are critical, as the outcomes give chiefs proof of the significance of representative fulfilment for firm execution and feature explicit areas of concentration, like authority, remuneration, and work/life balance. Moreover, the review highlights the developing significance of business audit sites in moulding hierarchical notorieties and proposes that HR divisions could use this pattern to all the more likely comprehend and address representative fulfilment. Generally speaking, the review adds to the current writing by offering exact proof of the positive job of worker fulfilment in unbiased and monetary firm-level execution, using an enormous and various example free of conventional rankings. Also, the review's attention on unambiguous features of occupation fulfilment improves how we might interpret what worker mentalities mean for authoritative results, giving significant bits of knowledge to the two scientists and professionals in the field of human assets the executives.
Oosthuizen, R. M., Coetzee, M., & Munro, Z. (2016) in their paper, "Work-life balance, job Satisfaction and turnover Intention amongst Information Technology Employees" address the crucial problem of talent retention in the information technology (IT) Sector, which is impacted by factors like globalisation, skills shortages, and rapid technological advancements. Examining the relationship between workers' perceptions of work-life balance, job happiness, and intention to leave is the goal of this study because employee turnover is costly and has negative effects. The study uses a random sample of 79 salaried IT professionals who are permanently engaged in a South African organisation. It employs measures such as the Turnover Intention Scale, the Minnesota Satisfaction Questionnaire, and the Survey Work-Home Interaction-Nijmegen. The study's participants, who are primarily married, white, and between the ages of 26 and 45, have been employed for more than ten years.
Their contributions to the analysis show a significant correlation between job satisfaction and the intention to leave one's job and experiences of both positive and negative work-home interactions. Interestingly, there is a strong correlation found between job satisfaction and the intention to leave. There is a difference in the relationship between job satisfaction and employee demographics such as race, marital status, and tenure, but no interaction effect between total work-life balance and job satisfaction and turnover intention is seen.
The findings show the necessity for customised approaches to accommodate the various requirements and experiences of IT professionals and emphasise the need to take into account the interaction between work-life balance, job satisfaction, and turnover intention in talent retention efforts.
Kasemsap's section (2017) digs into the meaning of occupation fulfilment inside present-day associations, clarifying its effect on different authoritative builds and areas, especially zeroing in on work execution, versatility, negative hierarchical issues, and the medical care industry. Work fulfilment, portrayed as representatives' perspectives towards their work and occupation-related exercises, assumes an essential part in holding ability inside associations. Elevated degrees of occupation fulfilment add to upgraded hierarchical efficiency, decrease worker turnover, and relieve work pressure, subsequently cultivating a positive working environment and supporting hierarchical incomes. The section highlights the significance for associations to devise precise administration and authority techniques pointed toward developing elevated degrees of occupation fulfilment among workers. At the point when workers experience work fulfilment, they are bound to display uplifted degrees of occupation execution, hence underlining the characteristic connection between work fulfilment and hierarchical achievement.
García, G. A., Gonzales-Miranda, D. R., Gallo, O., & Roman-Calderon, J. P. (2019) in their study, "Employee Involvement and job satisfaction: a tale of the millennial generation" examines the connection between job happiness and employee involvement among millennial workers in Colombia. The study uses ordered probit models to analyse data from a sample of 2103 millennial workers in different industries and regions in order to investigate the impact of employee involvement on general job happiness as well as particular aspects of job satisfaction. The results show that among millennial employees, job satisfaction and employee involvement are positively correlated. Additionally, the study shows that decisions about the organisation as a whole, as opposed to particular teamwork or primary task decisions, have a bigger positive effect on job satisfaction when more people participate in those decisions. Furthermore, millennial employees show a predilection for intrinsic components of their employment, like applying their knowledge to their work, which increases their pleasure in a collaborative setting. Despite noting certain limitations, such as the use of self-report data and the cross-sectional design of the study, the research adds to our understanding of the dynamics of job satisfaction and employee involvement, especially in the context of developing nations like Colombia. The study emphasises how important it is to take into account different employee participation models and how those models differ in how they affect various aspects of job happiness. These insights can be very helpful for companies trying to improve employee engagement and satisfaction among millennial workers.
Fidyah and Setiawati's review (2020) dives into the complicated elements of hierarchical culture (OC), representative commitment (EE), work fulfilment (JS), and representative execution (EP) inside the work environment setting. The exploration expects to investigate the immediate impacts of OC and EE on JS and EP, as well as the interceding job of JS in the connection between OC/EE and EP. Utilizing an example of 52 workers chosen through delineated irregular examining, the review utilizes an overview survey to assemble information, which is then broken down utilizing different measurable procedures including t-tests, F-tests, various straight relapse examinations, and way investigation. The discoveries of the review uncover a few huge connections and intercession impacts. OC, right off the bat, is found to fundamentally affect both JS and EP, demonstrating that a solid hierarchical culture adds to more elevated levels of occupation fulfilment and better representative execution. Likewise, EE is displayed to decidedly and fundamentally impact both JS and EP, recommending that drew-in workers will generally encounter higher work fulfilment and perform better in their jobs. Besides, the review shows that JS plays an interceding job in the connection between OC/EE and EP. This suggests that the impact of OC and EE on EP is to some degree communicated through their consequences for JS. At the end of the day, when representatives see a positive hierarchical culture or are exceptionally drawn in, they are bound to encounter more prominent work fulfilment, which thusly prompts further developed execution results. In general, the examination gives important experiences into the interconnectedness of hierarchical culture, representative commitment, work fulfilment, and worker execution. By uncovering these connections and intercession impacts, the review adds to a more profound comprehension of the elements that drive worker fulfilment and execution in the hierarchical setting. Moreover, the discoveries highlight the significance of encouraging a positive hierarchical culture and advancing worker commitment as techniques for improving both work fulfilment and execution inside the labour force.
Nabahani, P. R., & Riyanto, S. (2020), in their study, "Job Satisfaction and Work Motivation in Enhancing Generation Z’s Organizational Commitment" investigate the distinctive traits of Generation Z and how they affect organisational commitment.
Organisational dynamics will face difficulties and opportunities when Generation Z joins the workforce alongside older generations like Gen X and Gen Y. Notably, Gen Z is sometimes labelled as a "job hopper" generation since they frequently change occupations for a variety of reasons. There is a direct relationship between this behaviour and the idea of organisational commitment.
The purpose of the study is to investigate how Generation Z's organisational commitment is influenced by job satisfaction and work motivation. The research endeavours to offer companies insights on efficiently satisfying the needs of Generation Z in the workplace by comprehending their values and aspirations. The study used a desktop-based research methodology and used secondary data from books, journals, articles, and research papers to investigate the connection between work motivation, organisational commitment, and job satisfaction among Generation Z employees. Through this investigation, the study advances knowledge on how companies may develop and strengthen Generation Z workers' organisational commitment, which will ultimately improve workplace dynamics and retention tactics.
Putri, A. A., Dhewanto, W., & Nurdayat, I. F. (2020) in their study, "Understanding the Role of Job Satisfaction in Workplace from Millennial Generation’s Perspective toward Organizational Performance" explores the topic of job satisfaction in the Workplace from the viewpoint of the millennial generation, a substantial and expanding segment of the labour force. According to projections, the workforce composition of the global workforce by 2025 will be dominated by millennials and beyond, accounting for up to 75% of the workforce. Consequently, to sustain job satisfaction and organisational performance, organisations need to understand what attracts and keeps millennial talent. The goal of the study is to determine which aspects of job satisfaction have a major bearing on millennial workers' job happiness and the overall performance of the company. Using a questionnaire given by purposive sampling, data were gathered from 104 respondents working in the food and beverage sector in Bandung, Indonesia, who were millennials or members of Generation Y, or those between the ages of 19 and 39. The data were analysed using multiple linear regression analysis and descriptive analysis. The findings show that aspects of job satisfaction including coworkers, promotion, salary, and supervision have a major impact on organisational performance and together they account for a sizable amount (78.9%) of the variation in organisational performance. By advancing knowledge of the variables affecting millennial job satisfaction and how they affect company performance, this research helps to shape talent management and retention strategies for a workforce that is constantly changing.
Aziz et al's. study (2021) examines the connection between worker responsibility and occupation fulfilment inside private colleges in the Kurdistan area of Iraq. The examination means to inspect what hierarchical responsibility means for different work factors like turnover, authoritative citizenship conduct, and occupation execution. Factors, for example, job pressure, strengthening, position uncertainty, employability, and the reception of authority have been distinguished as affecting a representative's feeling of authoritative responsibility. Using a quantitative methodology, the review accumulates information from three distinct confidential colleges to investigate the connection between hierarchical responsibility and occupation fulfilment. The discoveries demonstrate that every one of the three autonomous elements considered is decidedly connected with work fulfilment. The outcomes recommend that upgrading position fulfilment can prompt expanded worker responsibility, in this way giving direction to college the board to work on hierarchical responsibility among representatives. Also, the review features the positive effect of occupation fulfilment on worker responsibility, stressing the significance of guaranteeing representative fulfilment to encourage authoritative responsibility. By and large, the exploration adds to understanding the exchange between worker responsibility and occupation fulfilment with regard to private colleges, offering bits of knowledge that can illuminate techniques pointed toward upgrading authoritative responsibility and further developing representative results.
Mgammal, M. H., and Al-Matari, E. M. (2021) conducted a study on "Survey data of coronavirus (COVID-19) thought concern, employees' work performance, employees' background, feeling about job, work motivation, job satisfaction, psychological state of mind, and family commitment in two Middle Eastern countries" offer a dataset examining various aspects related to the impact of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic on employees in two Middle Eastern countries. The dataset includes information on COVID-19 issues, work output, employee backgrounds, job motivation, job satisfaction, psychological well-being, and family commitment. A single survey that was administered in June and July 2020 to working people from various industries was used to gather data. 950 questionnaires were emailed out as part of the survey's online distribution method. Owing to the current situation, a combination of purposive and snowball selection methods was used to choose respondents. The final sample consisted of 307 replies from Yemen and Saudi Arabia, two Arabic nations. For data analysis, descriptive and inferential statistics were employed. This dataset adds to knowledge and understanding in these areas by offering insightful information about how the COVID-19 epidemic has affected several facets of the workplace, businesses, and workers' well-being.
Ninaus, K., Diehl, S., & Terlutter, R. (2021) in their study, "Employee perceptions of information and communication technologies in work life, perceived burnout, job satisfaction and the role of work-family balance" delves into the changing landscape of ICTs in the workplace and acknowledges that employees view ICTs as both resources and demands. The study creates an ICT demands-resources model based on the job-demands-resources model to investigate how these views affect job satisfaction, work-family balance, and burnout.
The study, which used three surveys—two pre-COVID-19 and one during—discovers that, on the whole, employees saw ICTs more firmly as resources than as demands. ICT resources, on the other hand, either had no (before to COVID-19) or very little (during COVID-19) positive effects on burnout and work-family balance, whereas ICT demands show a clear detrimental influence. Work-family balance helps to mitigate the detrimental impacts of ICT demands on burnout, according to mediation analyses. Furthermore, there is a connection between decreased job satisfaction and elevated burnout. Answers to qualitative surveys provide further information about how to enhance ICT use for work. Overall, the results highlight how crucial it is for businesses and staff to manage ICT demands over ICT resource management, highlighting the necessity of work-family balance and burnout mitigation techniques for better employee well-being and job satisfaction.
Xiu-Lan, T., Ho, T. C., Teo, P. C., Choo, L. S., & Rizal, A. M. (2021) in their paper, "Factors Affecting Job Satisfaction Among Young Employees in the Information & Communications Technology Sector in Malaysia," examine the various factors that influence job satisfaction in the Malaysian ICT industry with the goal of offering insights into retaining human capital. Through a review of the literature, they pinpoint a number of critical elements that affect young workers' job satisfaction, including work-related attributes like flexibility and work-life balance, opportunities for professional development and advancement, autonomy and feedback, supportive work environments, transformational leadership styles, and fair compensation and benefits. Organisations looking to improve employee satisfaction, hold onto talent, and stay competitive in the fast-paced ICT industry must recognise and take action on these aspects.
Yanchovska's review (2021) researches the connection between work fulfilment and individual execution among representatives in the IT area. The exploration means to investigate the relationship between occupation fulfilment and individual execution while additionally analyzing the general degree of representative fulfilment and possible contrasts in work fulfilment levels across segment gatherings. Using quantitative examination, the review assembles information from 126 worldwide respondents addressing more than 25 different IT organizations. Research strategies incorporate one-layered procedures for starter examination, Cronbach's alpha for unwavering quality appraisal, one-way ANOVA for looking at mean qualities, and connection investigation to inspect connections. The discoveries uncover a moderate yet genuinely critical connection between occupation fulfilment and representatives' very own exhibition, recommending a bidirectional impact that might be dependent upon different factors like work commitment, inspiration, stress, or weariness. Besides, most of the workers in the example express fulfilment with their positions. The concentrate likewise recognizes genuinely critical varieties in mean work fulfilment levels in light of segment factors like orientation and years in the ongoing position. The reasonable ramifications of the exploration highlight the significance of occupation fulfilment for representative maintenance, responsibility, and efficiency, underlining the requirement for associations to focus on establishing a spurring and favourable workplace. The review's creativity lies in its approval of the positive connection between occupation fulfilment and individual execution while adding to a more profound comprehension of occupation fulfilment elements among IT workers. Generally, the discoveries underscore the meaning of occupation fulfilment as a vital hierarchical incentive for accomplishing ideal business results and market initiative.
Almeida, M. P. D. (2022) in their research “IT Productivity Discrepancies: Impact on Job Satisfaction, Motivation and Burnout, in Multigenerational Employees" examines the consequences of variations in IT productivity across employees from different generations in their doctoral dissertation, As more Gen Zers enter the job, concerns about their IT skills and ability to get along with older generations surface. The purpose of this study is to clarify how working with coworkers who are of different generations and have varying levels of IT competence impacts workers' motivation, job satisfaction, and burnout. Applying a quantitative methodology, the study finds that differences in IT productivity have a major impact on motivation, work satisfaction, and burnout susceptibility. Interestingly, compared to earlier generations, younger generations feel more negative emotions, which lowers motivation and pleasure and increases the risk of burnout. This study highlights the need for solutions to offset intergenerational gaps in IT abilities for improved employee well-being and productivity, and it sheds insight into the issues these differences face in the workplace.
Budiman, Y., & Tan, P. H. P. (2022) researched, "The Influence of Job Stress, Job Satisfaction & Organizational Commitment Towards Turnover Intention for Millennials and Generation Z Employees in Internet Companies in Indonesia" explores the difficulties Indonesian internet companies face in coping with the high turnover rate among their Millennial and Generation Z workforce.
In addition to examining other possible elements that may contribute to turnover intention, the study attempts to determine the impact of job stress, job satisfaction, and organisational commitment on turnover intention. Partial Least Square - Structural Equation Modelling (PLS-SEM) was used to gather and analyse data from 103 respondents, who represented a range of job functions, genders, tenures within the organisation, and marital statuses.
The results show a strong correlation between organisational commitment, job stress, and job happiness. Additionally, occupational stress has a detrimental impact on organisational commitment and job satisfaction, which may provide problems for the effectiveness of the organisation. Furthermore, it has been discovered that among Millennials and Generation Z workers in internet organisations, organisational commitment has a major impact on their intention to leave. The present study illuminates the significance of stress management, job satisfaction, and organisational commitment in reducing the likelihood of turnover among younger workers in Indonesia's internet sector.
Dias et al. (2022) explore the interplay between work-life balance and job satisfaction, focusing on the organizational environment's impact on employee well-being. Recognizing the growing significance of employees' motivations, needs, and ambitions in today's business landscape, the authors highlight the importance for organizations to foster a positive and supportive environment that promotes employees' sense of belonging and well-being. They emphasize the role of organizations in facilitating a balance between professional and personal life for their employees. Drawing from a sample of 262 workers, the study's findings indicate that the organizational environment significantly influences both organizational commitment and job satisfaction. However, the authors did not find a significant impact of the organizational environment on the balance between professional and personal life. Furthermore, while there was a positive and significant relationship between organizational commitment and job satisfaction, no significant relationship was observed between organizational commitment and work-life balance. Additionally, organizational commitment was found to mediate the relationship between the organizational environment and job satisfaction, but not the relationship between organizational commitment and work-life balance. These findings underscore the complex dynamics at play in shaping employee perceptions of job satisfaction and work-life balance within organizational contexts, highlighting the need for further research and organizational initiatives aimed at promoting employee well-being and satisfaction.
Oktaviani's in his study (2022) distributed in the Jurnal Ekonomi Kreatif dan Manajemen Bisnis Computerized, the creator leads a deliberate writing survey and bibliometric examination to give an outline of occupation fulfilment and its related variables. Work fulfilment, a pivotal variable in human assets the board, mirrors the degree of happiness or uneasiness representatives experience in their positions, impacted by different persuading factors. The review intends to dive further into the idea of occupation fulfilment by utilizing the PRISMA strategy for precise audit and bibliometric examination procedures, zeroing in on articles from Science Direct and Emerald distributed somewhere in the range of 2017 and 2022. The screening system yielded 30 articles created by 95 people. The discoveries of the audit arranged work fulfilment-related factors into four principal classifications: authority, compensation, authoritative responsibility, and occupation stress. This complete examination fills in as a significant reference for future exploration tries, especially for scientists keen on investigating subjects connected with work fulfilment. By combining existing writing, this study adds to upgrading figuring out in the field and gives an establishment to additional insightful examinations concerning position fulfilment and its determinants.
Achmad, Noermijati, Rofiaty, and Irawanto's review (2023) investigates the complex connection between ability advancement, work fulfilment, representative commitment, and aim to remain among Age Z labourers, especially in the biggest modern place in Southeast Asia. The essential goal of the examination is to research whether ability improvement drives straightforwardly affect the aim of Age Z representatives to stay with their flow business for a drawn-out period. Moreover, the review plans to survey the interceding jobs of occupation fulfilment and representative commitment to this relationship. The hypothetical structure fundamental to the review places that compelling ability advancement practices can improve work fulfilment, representative commitment, and strengthening, eventually prompting expanded goals to remain among representatives. To examine these connections, the scientists gathered information from 342 Age Z workers across different ventures in Bekasi Rule, using purposive testing methods. The information examination was directed utilizing Brilliant PLS 3.0 programming. The discoveries of the review uncover a few significant bits of knowledge. First and foremost, the outcomes show a positive and critical connection between ability improvement and expectation to remain among Age Z labourers. Besides, the review distinguishes work fulfilment as a more huge middle person than a representative commitment to the connection between ability improvement and aim to remain. This recommends that the effect of ability improvement drives workers' expectation to remain generally intercedes through their degrees of occupation fulfilment. The exploration additionally features the reasonable ramifications of its discoveries, proposing that associations ought to focus on ability advancement endeavours to upgrade work fulfilment and, in this way, representative maintenance among Age Z labourers.
Besides, the review highlights the significance of leading further exploration with bigger examples of Age Z workers to acquire a more profound comprehension of their requirements and inclinations regarding ability improvement drives. All in all, this study adds to the current writing by revealing insight into the connection between ability advancement, work fulfilment, representative commitment, and expectation to remain among Age Z labourers.
By recognizing position fulfilment as a vital middle person in this relationship, the exploration offers significant bits of knowledge for associations looking to hold and draw in their young ability. Moreover, the review highlights the meaning of tending to the one-of-a-kind requirements of Age Z representatives in ability improvement systems, underscoring their significance to the achievement and maintainability of associations.
Rudy, R., Widjaja, B. T., & Tecoalu, M. (2023) in their study "The Effect of Job Satisfaction and Self-Efficacy on Organisational Commitment Mediated by Organisational Culture in Generation Z," examine the relationship between job satisfaction and self-efficacy and organisational commitment within the Generation Z age range, as mediated by organisational culture. Using IBM SPSS analysis, the study focuses on the Gojek or Grab courier community in Jabodetabek and investigates the correlations between these characteristics. In order to demonstrate the importance of these factors for organisational sustainability and profitability, the authors set out to investigate the effects of work satisfaction, self-efficacy, and organisational culture on organisational commitment. The empirical results show several significant conclusions: 1) Self-efficacy shows a strong influence on organisational commitment; 2) Job satisfaction does not significantly affect organisational commitment; 3. There is no substantial relationship between organisational culture and organisational commitment; 4. Job satisfaction and organisational culture do not significantly influence each other; 5. Self-efficacy does not significantly affect organisational culture; 6) The association between work satisfaction and organisational commitment is not mediated by organisational culture; 7) The relationship between self-efficacy and organisational commitment is not mediated by organisational culture. These results offer insightful information about the intricate relationships between job satisfaction, self-efficacy, organisational culture, and organisational commitment among Generation Z workers. They also have implications for management practices and organisational strategies meant to boost employee engagement and commitment in today's workplace.
Sagituly, G., & Guo, J. (2023) in their research, "Job satisfaction and organizational commitment: comparing Generations X and Y" examine the variations in work happiness and organisational commitment between the X and Y generations in Kazakhstan, a nation formed by the fall of the Soviet Union. By concentrating on workers who went through the shift from communist ideology to a newly created nation, the research seeks to understand the causes of generational differences in organisational commitment and job satisfaction. The study uses the Job Satisfaction Questionnaire (JSQ) and Organisational Commitment Questionnaire (OCQ) questionnaires with 605 participants from different government departments to evaluate the impact of generational traits. The results show that the two generations have different preferences and dissatisfactions: Generation X prioritises security and relationships with coworkers, while Generation Y places more importance on independence and supervision. Furthermore, Generation Y expresses unhappiness with a lack of originality, variety, and achievement, whereas Generation X is unhappy with activity, power, and pay. The results of the study largely corroborate the study's hypothesis, which states that for Generation X as opposed to Generation Y, extrinsic and intrinsic job satisfaction have larger positive correlations with commitment components. Notably, among Generation X, extrinsic job satisfaction is favourably correlated with commitment, whereas among Generation Y, internal job satisfaction is substantially correlated with commitment. These findings have ramifications for organisational strategies meant to improve employee engagement and offer insightful information about the generational dynamics of job satisfaction and organisational commitment and retention in the evolving workplace landscape of Kazakhstan.
Syal, A., Rosnani, T., Daud, I., Kalis, M. C. I., & Hendri, M. I. (2024) conducted a study on the topic, "The influence of reward, work-life balance on employee retention: The mediating effect of Job satisfaction Generation Z employees in West Kalimantan" investigates the factors that affect employee retention with a particular focus on Generation Z employees in West Kalimantan. This group is known for having low rates of loyalty and retention, which is frequently caused by a desire to explore professional possibilities and discontent with current roles. The purpose of the study is to examine the connections between employee retention, work-life balance, job satisfaction, and rewards. Utilising structural equation modelling (SEM) with AMOS 24 and explanatory quantitative research, the authors analyse data from 219 Generation Z workers in West Kalimantan's private trading organisations. The premise that rewards and work-life balance have a favourable impact on job satisfaction and employee retention is supported by the results. Furthermore, work-life balance or rewards and employee retention are mediated by job happiness, emphasising the critical role that job satisfaction plays in keeping Generation Z workers in the workforce. In the context of West Kalimantan's private trade organisations, this study offers insightful information about tactics for improving employee retention among Generation Z workers. It emphasises the significance of addressing job satisfaction through rewards and work-life balance programmes.
E. Identification Of Research Gaps
Although job happiness, employee engagement, and work-life balance have all been the subject of much research, there is still a significant knowledge vacuum on how these three factors interact in the setting of contemporary workplaces. This discrepancy is highlighted by several important factors:
- Holistic Analysis: Although work-life balance, employee engagement, and job happiness are frequently discussed separately in the literature currently in publication, there aren't many holistic studies that include these elements. There is a lack of research on the interactions and interplay between these factors, which makes it difficult to comprehend the complex dynamics that affect overall job satisfaction.
- Relevance in the Modern Era: Research that takes into account the changing nature of work and organizational structures in the digital age is essential. A lot of the research that has already been done may not fully reflect the special opportunities and problems that contemporary workers confront, especially when it comes to flexible work hours, remote employment, and the blending of home and professional lives.
- Intersectionality: There is much to learn about the intersections between work-life balance, employee engagement, and job happiness. The varied histories, identities, and experiences of workers are frequently overlooked in research, although these factors can have a big impact on how employees perceive and interact with their employers.
- Quantitative Analysis: Although qualitative research offers significant insights into personal experiences and viewpoints, few extensive quantitative studies closely analyze the connections between these variables. In addition to assisting in the identification of patterns and trends across various organizational contexts, quantitative analysis can provide a more thorough understanding of the strength and direction of relationships.
- Organizational Impact: Without thoroughly examining their organizational ramifications, many studies concentrate solely on individual-level outcomes, such as work satisfaction or employee well-being. For strategic management decisions to be informed, it is crucial to comprehend how work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction relate to larger organizational outcomes like productivity, retention, and performance.
F. Theoretical Underpinnings
A number of theoretical frameworks that offer a thorough understanding of the variables influencing employee well-being and organizational outcomes can be used to support research on work-life balance, job satisfaction, and employee engagement. Important theoretical stances consist of:
- Job qualities Model (JCM): The Job qualities Model (JCM), created by Hackman and Oldham, asserts that a number of job qualities affect motivation and job satisfaction. These characteristics include autonomy, skill variation, task identity, task relevance, and feedback. Through an analysis of the relationship between these job attributes and work-life balance as well as employee engagement, researchers can clarify the processes by which job design affects performance and overall job satisfaction.
- Social Exchange idea: According to this idea, relationships between people and organizations are built on the reciprocal exchange of resources, such as financial advantages (like pay and promotions) and social and emotional support (like respect and recognition). Using this theory, researchers can investigate how employees balance the costs and rewards of their contributions to the company, leading them to consider how perceptions of fairness, trust, and reciprocity affect job satisfaction, employee engagement, and work-life balance.
- Social Exchange idea: According to this idea, relationships between people and organizations are built on the reciprocal exchange of resources, such as financial advantages (like pay and promotions) and social and emotional support (like respect and recognition). Using this theory, researchers can investigate how employees balance the costs and rewards of their contributions to the company, leading them to consider how perceptions of fairness, trust, and reciprocity affect job satisfaction, employee engagement, and work-life balance.
- Dual-Process Model of Job Stress: The Dual-Process Model of Job Stress makes a distinction between the impact of job resources—such as social support and autonomy—and job demands—such as workload and time pressure—on the well-being of employees. Through an examination of the relationship between job demands and resources, researchers may evaluate how work-related stressors affect job satisfaction and engagement. They can also identify ways in which organizations can reduce these impacts by allocating resources and creating supportive work environments.
- Conservation of resources (COR) theory: The conservation of resources (COR) theory holds that people work hard to gather, safeguard, and hold onto important resources, such as social, psychological, and physical resources.
Using this theory, researchers can look at how resource buildup or depletion impacts work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction, especially when it comes to personal, professional, and job-related resources.
II. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Scope Of The Study
- This study's scope includes the investigation of job happiness among contemporary workers, with a particular emphasis on work-life balance and employee engagement.
- Employees from a variety of industries will be included in the study, with a focus on those that are going through major shifts in expectations and work patterns, like technology, healthcare, finance, and education.
- It will look into how work-life balance and employee engagement affect job satisfaction while taking a variety of demographic variables like age, gender, education level, and job role into account.
- The research will investigate the work-life balance and employee engagement strategies used by the organization through policies, practices, and initiatives.
- Its objective is to evaluate the efficacy of various approaches, including wellness programs, flexible work schedules, and staff development plans, in raising job satisfaction.
- The study will look at how employee performance, job satisfaction, and organizational outcomes like productivity, retention rates, and overall success are related to one another.
- The investigation of potential moderating or mediating variables that might affect the relationship between work-life balance, job satisfaction, and employee engagement is also included in the scope.
- In order to enhance job satisfaction, employee well-being, and overall organizational success in the contemporary workplace, the study aims to offer insights that can guide organizational practices and policies.
B. Research Objectives
- To examine the several elements—intrinsic and extrinsic—that affect employees' job satisfaction in the modern workplace.
- To examine how engaged workers view their work and how it fits with company objectives to determine how employee engagement affects job satisfaction as an independent variable.
- To analyse the dynamics of work-life balance and how they impact employee satisfaction, with a special emphasis on the relationship between employees' job satisfaction and their capacity to manage personal and professional obligations.
- To examine the connections between work-life balance, job happiness, and employee engagement to spot any underlying trends or interdependencies.
- To perform a comprehensive investigation of work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction in today's workplaces, bridging the information gap about how these elements interact and influence one another.
- To investigate the interplay between work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction while taking into account the diverse backgrounds, identities, and experiences of employees and how they affect how they are perceived by and interact with employers.
- To use quantitative analysis approaches to provide a thorough understanding of the linkages between work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction, allowing the detection of trends.
C. Framing Of Research Hypotheses
- HYPOTHESES 1
- Hypothesis (H0): There is no significant relationship between employee engagement and job satisfaction among modern employees.
- Hypothesis (H1): There is a significant relationship between employee engagement and job satisfaction among modern employees.
2. HYPOTHESES 2
- Hypothesis (H0): There is no significant relationship between work life balance and job satisfaction among modern employees.
- Hypothesis (H1): There is a significant relationship between work life balance and job satisfaction among modern employees.
3. HYPOTHESES 3
- Hypothesis (H0): There is no significant difference in job satisfaction among employees with different levels of both employee engagement and work-life balance.
- Hypothesis (H1): There is a significant difference in job satisfaction among employees with different levels of both employee engagement and work-life balance.
D. Research Design
- Research Approach: This study uses a quantitative strategy to gather information from participants through questionnaire surveys. The collected structured data will undergo statistical analysis to investigate the connections among work-life balance, job satisfaction, and employee engagement.
- Type of Research: Quantitative research is used because it enables the measurement and study of variables using numerical data. It is possible to test hypotheses and find patterns or connections between variables by using structured questionnaire surveys.
- Methodology: Participants' responses to a questionnaire survey will be gathered for data collection. Based on the goals of the research described in Chapter 1, the questionnaire will be created to gather information about participants' views of work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction. Likert scales or alternative suitable response formats will be used for the questionnaire items to gather participants' opinions and perceptions.
- Analysing Data: To examine the information gathered from the questionnaire survey, quantitative analytic techniques will be used. Every question on the survey will be looked over to find any trends or recurring themes in the information. The associations between work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction will be investigated using statistical methods like regression analysis and correlation analysis. The goals and theories of the study will be taken into consideration while interpreting the findings.
- Method of Sampling: A representative sample of participants from the target demographic—which consists of workers from a variety of industries in modern work environments—will be used in this study. A stratified random sampling technique will be used to guarantee sample variety. This methodology will consider many demographic factors, including job function, gender, age, and years of experience, to guarantee that the sample fairly represents the variety found in the intended audience.
E. Methods For Data Collection & Variables Of The Study
- Questionnaire Survey:
- A structured questionnaire will be designed to collect information from participants about work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction.
- Questionnaire topics about employee perceptions of work-life balance are included.
- Additionally, employee engagement questions are examined such as passion for work duties, dedication to organisational goals, and satisfaction with communication and teamwork.
- Job satisfaction is assessed using questions regarding overall satisfaction with employment roles and responsibilities.
- Likert scales or other suitable response formats will be used in the questionnaire to record participants' thoughts and perceptions.
- To reach a bigger and more diverse range of participants, the survey will be done online.
2. Secondary Data Analysis:
- In addition to the primary data collected through the questionnaire survey, secondary data analysis was also conducted.
- Existing literature, organisational records, and pertinent reports was examined to gain further insight into work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction.
F. Variables
- Independent Variables:
- Work-Life Balance Initiatives: This variable includes organisational initiatives and policies meant to encourage employees in modern work settings to maintain a work-life balance.
- Employee Engagement Practices: This variable comprises the strategies and programmes that companies use to encourage worker engagement at work.
2. Dependent Variables:
Job Satisfaction: This variable assesses how satisfied workers are overall with their jobs and work environments.
3. Control Variables:
- Demographic Variables: The control variables that will be incorporated are age, gender, education level and years of work experience. These demographic factors will assist in adjusting for possible variations in answers depending on personal traits.
- Organizational Factors: Control variables will include organisational size and organisational culture. These factors may have an impact on perceptions of work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction.
III. DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION
A. Techniques For Data Analysis
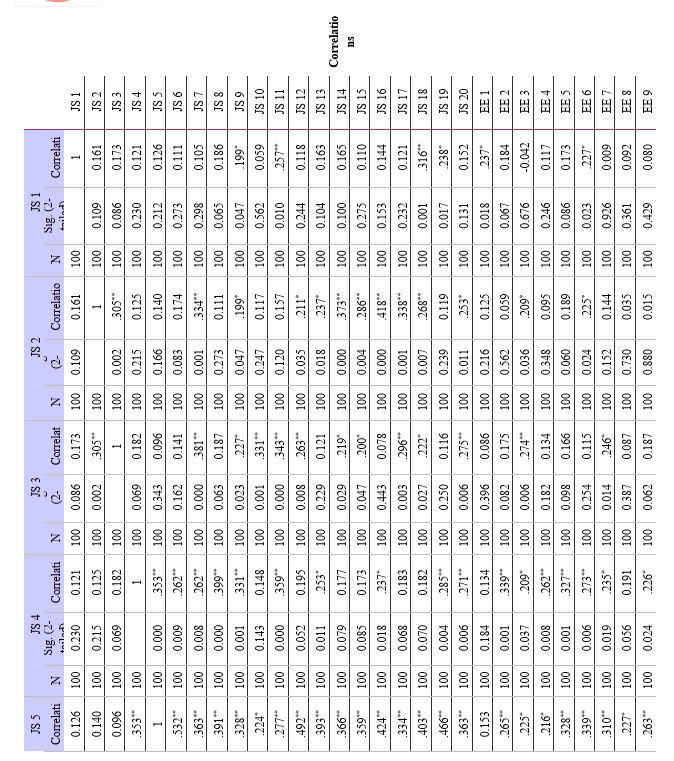
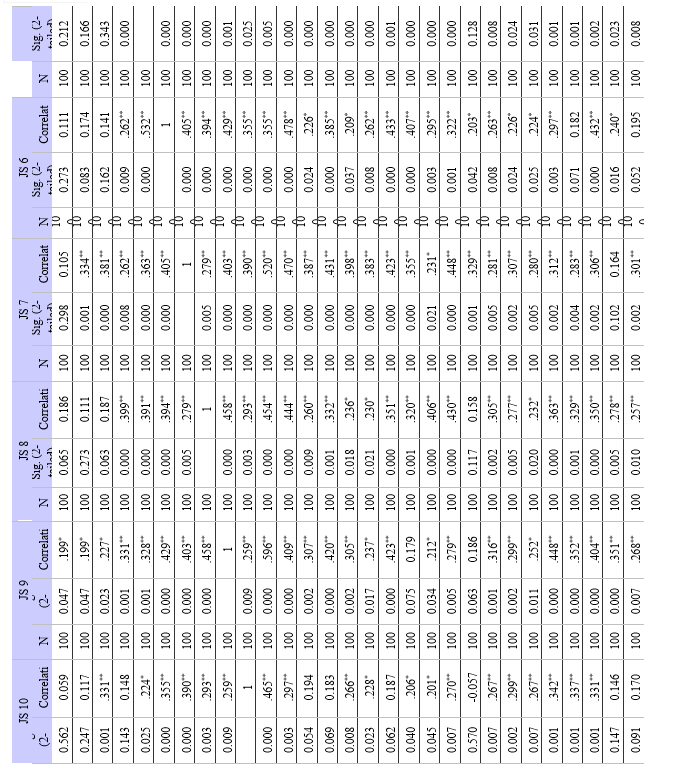
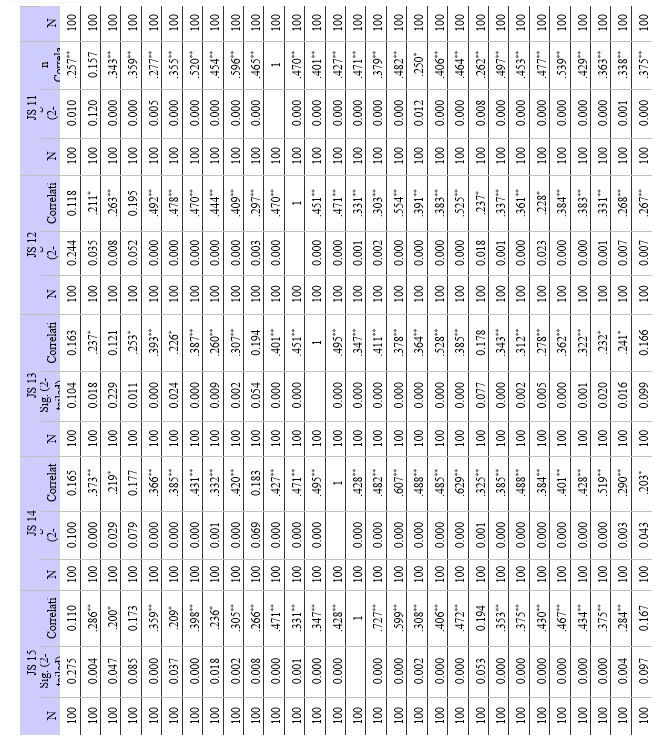
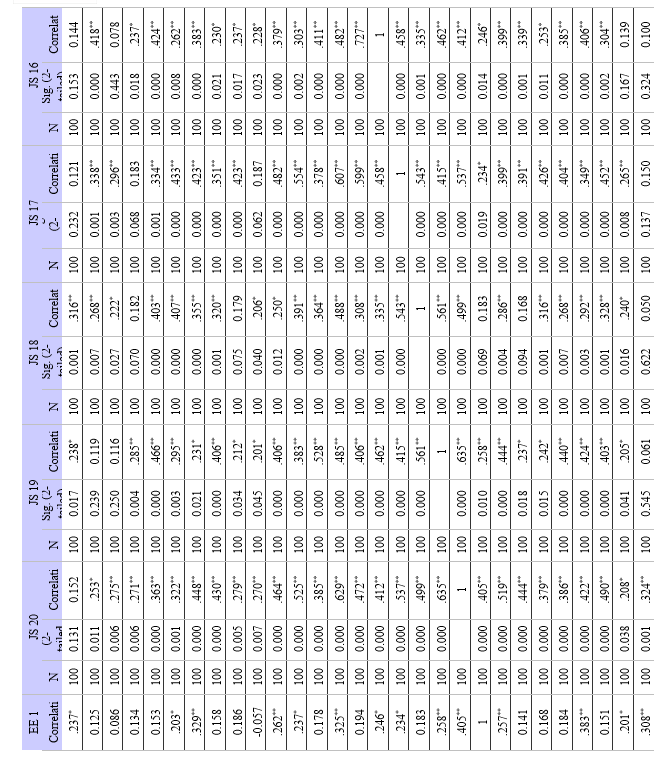
- Correlation Analysis: This method evaluates the direction and strength of a link between two or more variables. Correlation analysis has been employed in this study to look at the degree of relationship between variables like work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction. Correlation coefficients, such as Pearson's correlation coefficient, are used to assess whether there is a positive, negative, or non existent association between two variables. By pointing out possible trends and connections between variables, correlation analysis establishes the framework for more research.
- ANOVA (Analysis of Variance): An analysis of variance, or ANOVA, is a statistical method for comparing means between two or more groups. ANOVA has been used in the study to determine whether employees who were divided into distinct groups according to attributes like work-life balance, employee engagement, demographics, or organisational characteristics had significantly different job satisfaction scores. In particular, one-way or factorial ANOVA would have been performed by researchers to ascertain whether group differences or other relevant factors account for the variation in work satisfaction levels. ANOVA facilitates the identification of group differences and offers information on potential influencing factors for job satisfaction.
B. Hypotheses Testing And Methods
- Hypotheses Testing
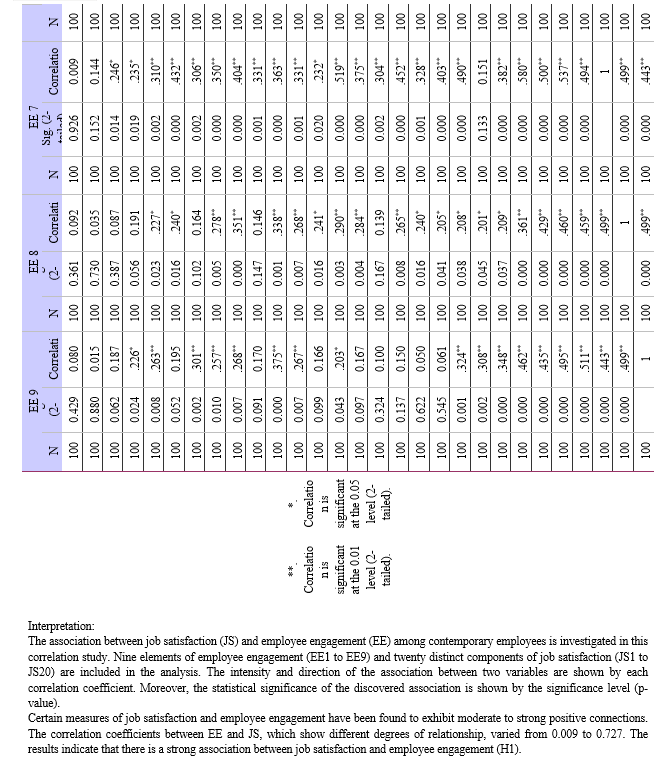
a. Hypothesis 1 - Relationship between Employee Engagement and Job Satisfaction:
- Null Hypothesis (H0): There is no significant relationship between employee engagement and job satisfaction among modern employees.
- Alternative Hypothesis (H1): There is a significant relationship between employee engagement and job satisfaction among modern employees.
- Method: Correlation analysis is used to determine the degree and direction of the association between employee engagement and job satisfaction. A significance level (alpha) of 0.01 is used to calculate the correlation coefficient and assess statistical significance.
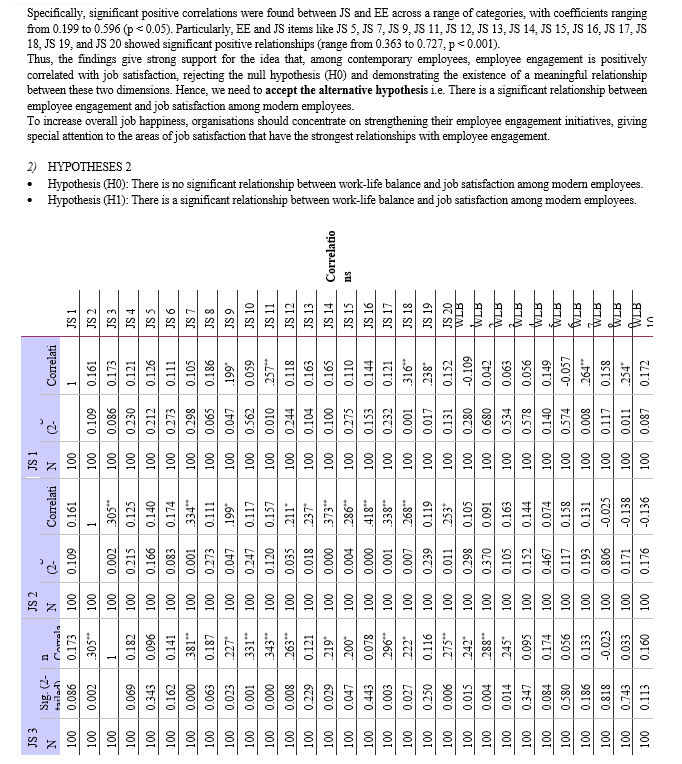
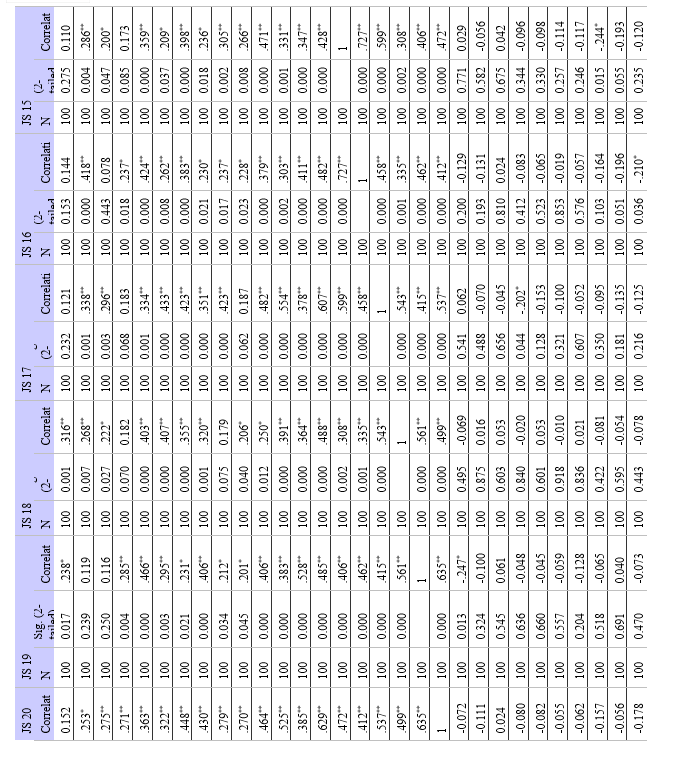
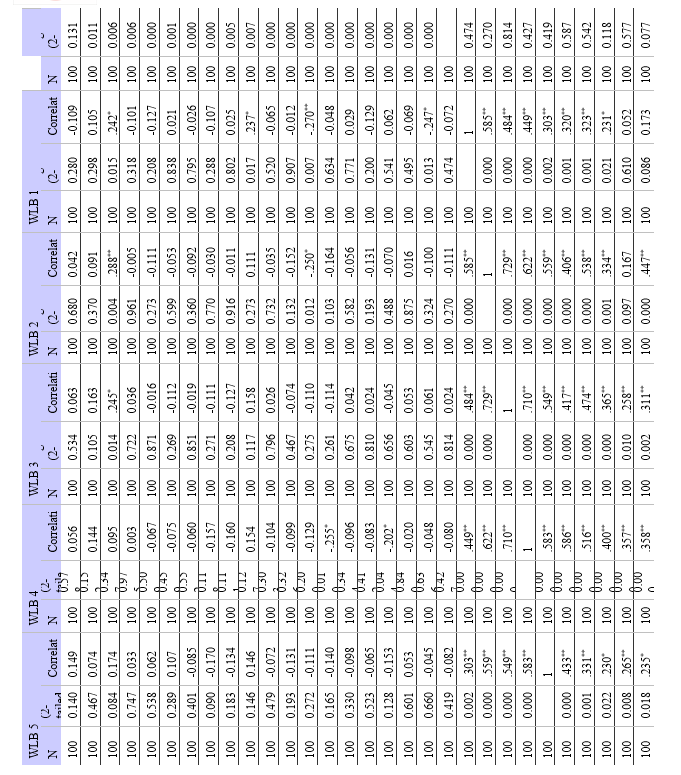
b. Hypothesis 2 - Relationship between Work-Life Balance and Job Satisfaction:
- Null Hypothesis (H0): There is no significant relationship between work-life balance and job satisfaction among modern employees.
- Alternative Hypothesis (H1): There is a significant relationship between work-life balance and job satisfaction among modern employees.
- Method: Correlation analysis would be used, just like in the first hypothesis, to determine whether work-life balance and job satisfaction are related. The correlation coefficient is calculated, and statistical significance is determined.
c. Hypothesis 3 - Differences in Job Satisfaction based on Employee Engagement and Work-Life Balance:
- Null Hypothesis (H0): There is no significant difference in job satisfaction among employees with different levels of both employee engagement and work-life balance.
- Alternative Hypothesis (H1): There is a significant difference in job satisfaction among employees with different levels of both employee engagement and work-life balance.
- Method: ANOVA was used to compare the means of job satisfaction scores across groups classified according to employee engagement and work-life balance.
2. Methods
a. Correlation Analysis: This method evaluates the direction and strength of a link between two or more variables. To determine the degree of relationship between variables like work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction, correlation analysis was used in this research.
b. ANOVA: This study used ANOVA, a statistical method for comparing means among several groups. Its objective was to ascertain whether job satisfaction scores among employees categorised by work-life balance, employee engagement, demographics, or organisational characteristics differed significantly from one another.








IV. FINDINGS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
A. earch Outcome And Findings
- Data Interpretation:
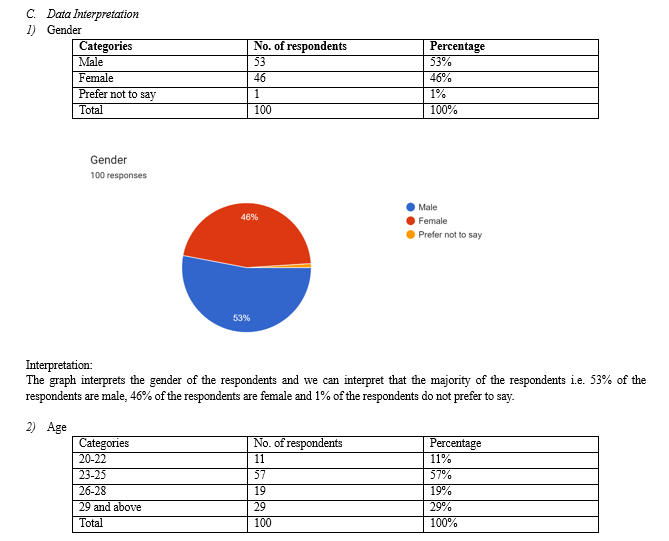
a. Gender Distribution: Male respondents constitute the majority (53%), followed by female respondents (46%), and a small fraction (1%) of those who would prefer not to divulge.
b. Age Distribution: With 57% of respondents, the largest age group is 23–25 years old. This is followed by 29 and older (29%), 26–28 years old (19%), and 20–22 years old (11%).
c. Total Work Experience: The majority of respondents (57%), had worked for less than two years, then for three to five years (28%), six to eight years (6%), and nine years or more (9%).
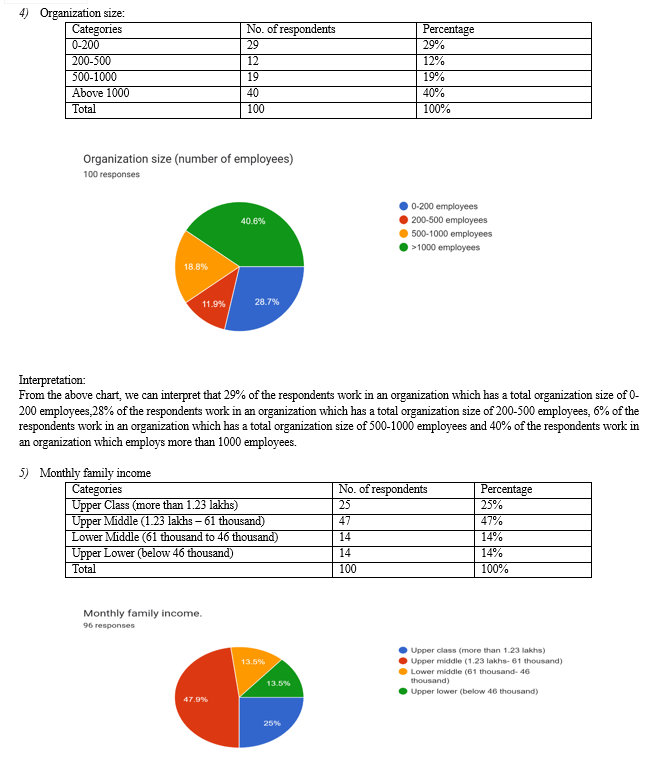
d. Organization Size: More than forty percent of respondents work for companies employing more than a thousand people. These companies are followed by those with 0-200 employees (29%), 500-1000 employees (19%), and 200-500 employees (12%).
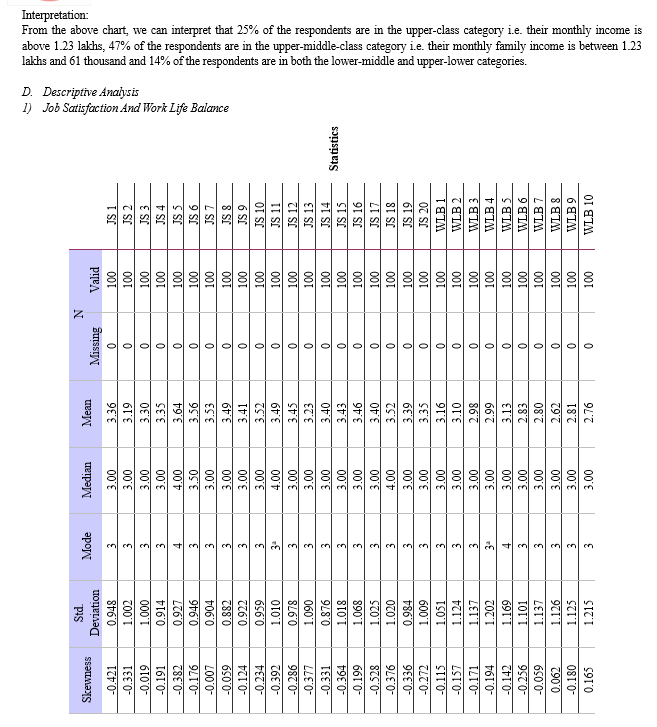
e. Monthly Family Income: Upper class (25%), lower middle class (14%), upper lower class (14%), and over half of the respondents (47%) are classified as upper middle class.
2. Descriptive Analysis
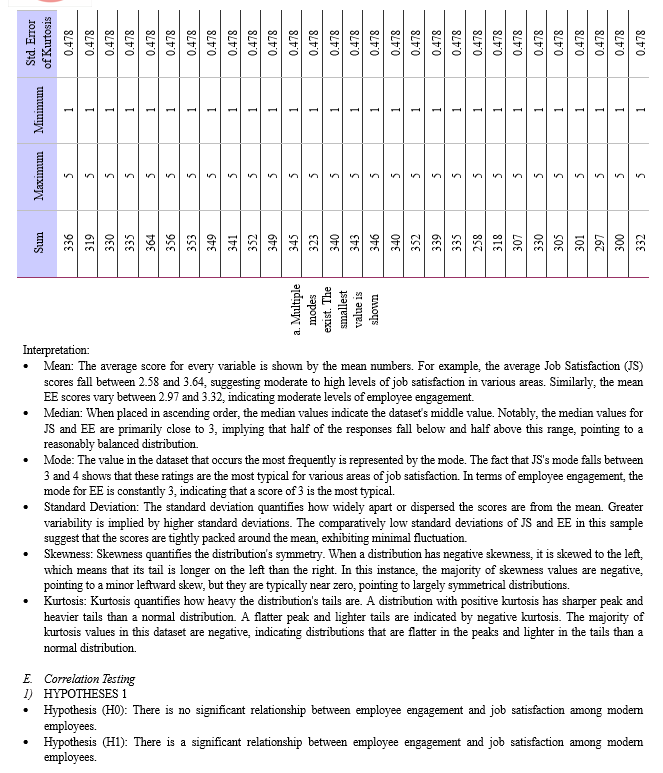
a. Job Satisfaction (JS):
- Mean JS scores range from 2.62 to 3.64, indicating variations in perceptions of work satisfaction.
- Median values suggest symmetrical distributions for JS.
- Modes typically lie between 3 and 4 for JS, indicating commonly chosen values.
- Standard deviation scores for JS range from 0.882 to 1.215, indicating heterogeneity in responses.
- Skewness and kurtosis values show variations in the distributional shape of JS, suggesting different patterns of response tendencies.
b. Work-Life Balance (WLB):
- Mean WLB scores range from 2.76 to 3.56, indicating variations in perceptions of work-life balance.
- Median values suggest symmetrical distributions for WLB.
- Modes typically lie between 3 and 4 for WLB, indicating commonly chosen values.
- Skewness and kurtosis values show variations in the distributional shape of WLB, suggesting different patterns of response tendencies.
c. Employee Engagement (EE):
- The mean scores for JS and EE range from 2.58 to 3.64, indicating the average level of satisfaction or engagement across different dimensions.
- The median values are mostly around 3 for both JS and EE, indicating that half of the respondents rated their satisfaction or engagement at or above this value.
- The mode represents the most frequent score in each aspect. The modes for both JS and EE are predominantly 3.
- The standard deviations are relatively low, indicating that most respondents' scores are clustered closely around the mean.
3. Hypothesiss Testing
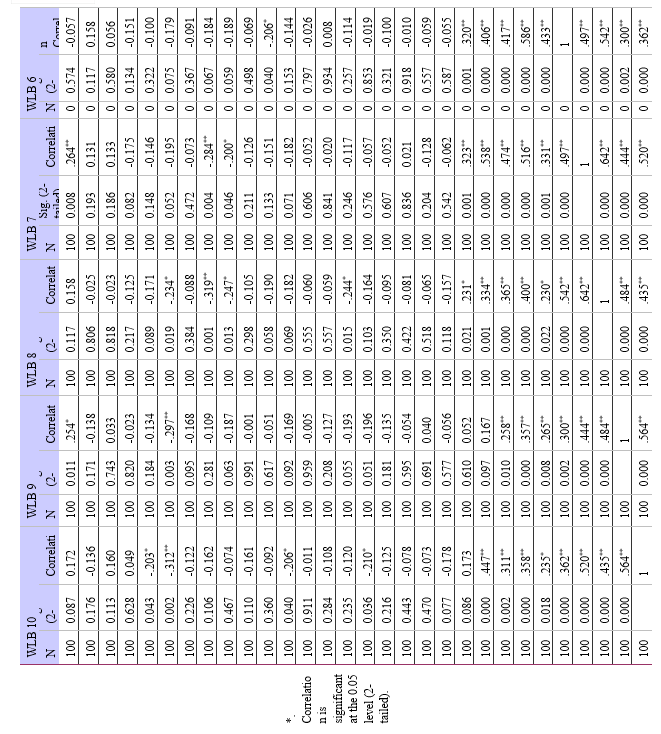
a. Relationship between Employee Engagement and Job Satisfaction: Strong positive relationships between work satisfaction and employee engagement were found in the study. This suggests that among modern employees, job satisfaction tends to improve along with levels of employee engagement. This is a significant discovery because it implies that companies that engage in employee engagement techniques would probably witness increases in workers' general job satisfaction levels.
b. Relationship between Work-Life Balance and Job Satisfaction: Relationship between Job Satisfaction (JS) and Work-Life Balance (WLB): The study also found some statistically significant positive correlations between job satisfaction and work-life balance variables. Accordingly, those who believe they have a better work-life balance typically express more job satisfaction. A supportive workplace culture, flexible work schedules, a manageable workload, and access to resources that support employees in successfully juggling their personal and professional lives are just a few of the elements that make up work-life balance.
c. Differences in Job Satisfaction based on Employee Engagement and Work-Life Balance: The findings of the ANOVA revealed notable variations in work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction among the samples.
4. Key Findings:
a. Employee Engagement and Job Satisfaction: There is a strong positive correlation between employee engagement and work happiness among modern employees. Increased job satisfaction and engagement typically go hand in hand.
b. Work-Life Balance and Job Satisfaction: Work-life balance (WLB) and job satisfaction (JS) were found to have statistically significant positive relationships. Finding a strong correlation between JS and several WLB components highlights the significance of striking a work-life balance for overall job satisfaction. The findings provided support to the alternative hypothesis (H1), highlighting the need of resolving concerns related to work-life balance in order to improve employee job satisfaction.
c. Impact of Employee Engagement and Work-Life Balance on Job Satisfaction: Employee engagement and work-life balance both have a strong influence on job satisfaction. However, there is no visible effect of their interactions on job satisfaction levels.
To conclude, Employee involvement positively impacts job satisfaction, emphasising the need for engagement-enhancing methods. And there is also a positive correlation between work-life balance and job satisfaction. Work-life balance and employee engagement are both important components that affect job satisfaction, but their combined impact is stronger. To increase workers' overall job happiness, organisations should prioritise enhancing work-life balance programmes and employee engagement strategies.
B. Theoretical Implication
1. Job Satisfaction and Organizational Well-being: The study highlights that one of the most important factors in predicting an organization's success is work happiness. Through an examination of factors that influence job happiness, such as work-life balance and employee engagement, the research offers valuable insights into how companies can cultivate positive work cultures that promote employee satisfaction.
2. Employee Engagement as a Driver of Job Satisfaction: Based on research conducted and the Social Exchange Theory, the study emphasises the beneficial correlation between job satisfaction and employee engagement. This emphasises how crucial it is to have an engaged staff by implementing tactics that encourage dedication, zeal, and alignment with company objectives.
3. Work-life Balance and Employee Well-being: The study emphasises how important it is to strike a balance between work and personal obligations in order to improve employee wellbeing and job satisfaction. This is consistent with theories like the Conservation of Resources (COR) theory, which highlights the value of protecting and restocking one's own resources in order to reduce burnout and improve job satisfaction.
4. Intersectionality and Diversity: The study recognises the diversity of the workforce and its possible influence on views of work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction by taking into account demographic characteristics including age, gender, and organisational aspects. This emphasises how customised organisational solutions that take into account a range of needs and preferences are necessary.
5. Practical Implications for Organisational Policies: The goal of the study is to give organisations useful information on how to raise work-life balance, job satisfaction, and employee engagement. The research provides evidence-based recommendations for organisational policies and practices targeted at improving employee well-being and organisational effectiveness by reviewing the body of existing literature and empirical data.
6. Quantitative Analysis and Research Methodology: To examine the correlations between important variables, the study uses quantitative research techniques, such as statistical analysis and questionnaire surveys. This methodological technique makes it possible to identify patterns or trends in a variety of organisational situations and to rigorously examine causal linkages.
C. Managerial Implication
- Tailored Employee Engagement Strategies: Based on the study's findings, managers can create employee engagement plans that are specifically designed to pique workers' passion, dedication, and feelings of purpose. Managers can create programmes that complement employees' intrinsic motivators and organisational objectives by knowing the elements that lead to employee engagement, such as purposeful work assignments and chances for skill development.
- Flexible Work Arrangements: Managers can adopt flexible work arrangements like telecommuting, flexible hours, and reduced workweeks because they understand how important work-life balance is to improving job satisfaction and well-being. Organisations may foster a better work-life balance and raise employee satisfaction levels by giving workers more control over their schedules and enabling them to manage work and personal commitments.
- Resource Allocation and Support: Managers have the authority to provide funding for projects aimed at promoting the well-being of their workforce, including wellness initiatives, employee assistance programmes, and chances for professional growth. Organisations may lower burnout, raise job satisfaction, and increase employee retention by funding programmes that support mental, emotional, and physical wellness.
- Promoting Inclusivity and Diversity: Managers can encourage inclusivity and diversity inside the company by acknowledging the influence of demographic factors on opinions of work-life balance and job satisfaction. Organisations may establish a supportive and empowered work environment for all employees by promoting an inclusive culture that values and respects varied opinions.
- Continuous Feedback and Communication: To make sure that workers' needs and concerns are met, managers should create open lines of contact and give them feedback frequently. Managers can improve job happiness and engagement by identifying areas for improvement and implementing targeted interventions by asking workers about their work experiences.
- Training and Development: To give staff members the tools and resources they need to be successful in their positions, managers might fund training and development initiatives. Organisations may foster a culture of ongoing learning and development and boost employee engagement and job satisfaction by giving employees opportunities for growth and progress.
- Performance Recognition and Rewards: To recognise and honour staff members' accomplishments and contributions, managers should put in place programmes for performance recognition and awards. By acknowledging employees' contributions and offering substantial incentives, companies can cultivate a climate of gratitude and inspiration that amplifies workplace contentment and involvement.
D. Limitations Of The Study
- Self-reporting and Social Desirability Bias: The study's use of self-reported data through questionnaire surveys may be vulnerable to social desirability bias, in which participants may give responses consistent with expectations or standards from society rather than reflecting their actual experiences or perceptions. The reliability and accuracy of the data gathered may be impacted by this bias.
- Cross-sectional Design: The study's cross-sectional design, which involves gathering data all at once, can make it more difficult to identify the causes of the variables. Experiments or longitudinal designs would offer stronger proof of causality and enable a more thorough comprehension of how variables change over time and affect work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction.
- Measurement Error and Validity: Measurement error and construct validity difficulties may arise from the study's dependence on questionnaire surveys to assess variables like work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction. To guarantee the accuracy of the results, a thorough evaluation of the validity and reliability of the survey instruments used to assess these constructs is necessary.
- Response Rate and Non-Response Bias: The percentage of invited participants who finished the survey, or the study's response rate, may have an effect on the sample's representativeness and introduce non-response bias. The results may not fairly represent the opinions of the whole workforce if some employee groups are more likely than others to reply to the survey.
- Limited Scope of Variables: Although the study looks at important variables like work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction, it might miss additional relevant variables that could have an impact on organisational outcomes and employee well-being.
E. Conclusion
To conclude, this study examined the relationships between work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction in contemporary workplaces, with an emphasis on the IT sector. The study created research hypotheses to explore the correlations between these variables after conducting a thorough evaluation of the literature to identify gaps in the field.
By using a quantitative research methodology, secondary data analysis and questionnaire surveys were used to gather data. The study's conclusions showed a strong relationship between job satisfaction and employee engagement, underscoring the need to encourage staff involvement to raise overall job satisfaction. Even though there was less of a correlation, there was still a favourable association between work-life balance and job satisfaction, highlighting the importance of encouraging a healthy balance between work and personal duties in modern work environments.
Furthermore, the research revealed significant differences in work-life balance, employee engagement, and satisfaction with work amongst various demographic categories and organisational sizes. These results highlight the necessity of customised approaches to meet employees' varied requirements and preferences in order to promote a welcoming and inclusive workplace environment.
The study's theoretical implications emphasised the significance of work-life balance and employee engagement in fostering both organisational success and employee well-being, as well as the role that job satisfaction plays in organisational well-being. Managerial implications also emphasised the necessity of customised employee engagement plans, adaptable work schedules, allocating resources for employee assistance, and encouraging inclusivity and diversity in the workplace.
The cross-sectional design, measurement inaccuracy, potential biases in self-reporting, and the narrow range of factors looked at were among the study's noted drawbacks. Future studies addressing these constraints will contribute to our growing understanding of the intricate relationships among work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction.
As a result, this research study offers insightful information about the variables affecting job satisfaction in contemporary workplaces and offers organisations actionable suggestions for improving both organisational success and employee well-being. Organisations can establish work cultures that promote employee satisfaction, productivity, and long-term success by placing a high priority on employee engagement, promoting work-life balance, and valuing diversity and inclusion.
F. Scope For Future Research
- Comparative Studies Across Industries and Cultures: Comparative research across various industries and cultural contexts may shed light on the ways that various organisational settings differ in terms of work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction. Researchers can find both context-specific and universal principles that affect employee well-being by comparing findings across industries and nations.
- Technology and Remote Work: Future studies may examine the effects of technology on work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction in light of the growing use of remote work and digital technologies. Research initiatives may examine how employees' experiences in the digital workplace are influenced by boundary management techniques, flexible work schedules, and virtual collaboration tools.
- Family-Friendly Policies: Studies could concentrate on how well work-life balance and job satisfaction are promoted by family-friendly policies including flexible scheduling, childcare support, and parental leave. Through the analysis of these policies' effects on worker satisfaction, productivity, and retention, academics can provide valuable insights for public policy and organisational practices.
- Diversity and Intersectionality: Future studies could take an intersectional approach to investigate the relationships between work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction and variables like gender, race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic position. Through the consideration of the distinct experiences of varied populations, scholars can detect inequalities and formulate comprehensive approaches to foster fairness and welfare in the work environment.
- Employee Well-Being and Performance Outcomes: Future studies should examine the connections between work-life harmony, job satisfaction, and employee engagement and how these linkages affect workers' well-being and performance. Research could look at how happy and involved workers support the productivity, creativity, and success of the company.
- Globalization and Remote Work Trends: The workforce is becoming more globally integrated, and remote work arrangements are becoming more common. Future studies should look into how these trends affect work-life balance, employee engagement, and job satisfaction. In a global setting, research might examine the effects of virtual teams, cross-cultural communication, and flexible work arrangements on employee experiences and organisational results.








References
[1] Hu, N., Poon, S., Zhong, J., & Wan, Y. (2004). Job Satisfaction of Information Technology Professionals. [2] Kamalanabhan, T. J., Sai, L. P., & Mayuri, D. (2009). Employee engagement and job satisfaction in the information technology industry. Psychological reports, 105(3), 759-770. [3] Kanwar, Y. P. S., Singh, A. K., & Kodwani, A. D. (2009). Work—life balance and burnout as predictors of job satisfaction in the IT-ITES industry. Vision, 13(2), 1-12. [4] Hussin, A. (2011). The relationship between job satisfaction and job performance among employees in tradewinds group of companies (Doctoral dissertation, Open University Malaysia). [5] Kassim, E. S., Ali, S. A. M., Jalaini, S. F. A. K., Said, N. A., Ab Latiff, D. S., & Salleh, F. (2013, June). Work life balance and job satisfaction: How relevant are they?. In 2013 International Conference on Technology, Informatics, Management, Engineering and Environment (pp. 62-66). IEEE. [6] Melián-González, S., Bulchand-Gidumal, J., & Gonzalez Lopez-Valcarcel, B. (2015). New evidence of the relationship between employee satisfaction and firm economic performance. Personnel Review, 44(6), 906-929. [7] Oosthuizen, R. M., Coetzee, M., & Munro, Z. (2016). Work-life balance, job satisfaction and turnover intention amongst information technology employees. Southern African Business Review, 20(1), 446-467. [8] Kasemsap, K. (2017). The significance of job satisfaction in modern organizations. In Handbook of research on human factors in contemporary workforce development (pp. 181-200). IGI Global [9] García, G. A., Gonzales-Miranda, D. R., Gallo, O., & Roman-Calderon, J. P. (2019). Employee involvement and job satisfaction: a tale of the millennial generation. Employee Relations: The International Journal, 41(3), 374-388. [10] Fidyah, D. N., & Setiawati, T. (2020). Influence of organizational culture and employee engagement on employee performance: job satisfaction as intervening variable. Review of Integrative Business and Economics Research, 9(4), 64-81. [11] Nabahani, P. R., & Riyanto, S. (2020). Job satisfaction and work motivation in enhancing generation Z’s organizational commitment. Journal of Social Science, 1(5), 234-240. [12] Putri, A. A., Dhewanto, W., & Nurdayat, I. F. (2020). Understanding the role of job satisfaction in workplace from millennial generation’s perspective toward organizational performance. KnE Social Sciences, 1047-1063. [13] Mahmood Aziz, H., Jabbar Othman, B., Gardi, B., Ali Ahmed, S., Sabir, B. Y., Burhan Ismael, N., ... & Anwar, G. (2021). Employee commitment: The relationship between employee commitment and job satisfaction. Aziz, HM, Othman, BJ, Gardi, B., Ahmed, SA, Sabir, BY, Ismael, NB, Hamza, PA, Sorguli, S., Ali, BJ, Anwar, G.(2021). Employee Commitment: The Relationship between Employee Commitment And Job Satisfaction. Journal of Humanities and Education Development, 3(3), 54-66. [14] Mgammal, M. H., & Al-Matari, E. M. (2021). Survey data of coronavirus (COVID-19) thought concern, employees\' work performance, employees background, feeling about job, work motivation, job satisfaction, psychological state of mind and family commitment in two middle east countries. Data in brief, 34, 106661 [15] Ninaus, K., Diehl, S., & Terlutter, R. (2021). Employee perceptions of information and communication technologies in work life, perceived burnout, job satisfaction and the role of work-family balance. Journal of Business Research, 136, 652-666. [16] Xiu-Lan, T., Ho, T. C., Teo, P. C., Choo, L. S., & Rizal, A. M. (2021, December). Factors Affecting Job Satisfaction Among Young Employees in the Information & Communications Technology Sector in Malaysia. In 2021 International Conference on Decision Aid Sciences and Application (DASA) (pp. 414-418). IEEE. [17] Yanchovska, I. (2021). The relationship between job satisfaction and individual performance of IT employees. Proceedings of CBU in Economics and Business, 2, 141-148. [18] Almeida, M. P. D. (2022). IT productivity discrepancies: impact on job satisfaction, motivation and burnout, in multigenerational employees (Doctoral dissertation). [19] Budiman, Y., & Tan, P. H. P. (2022). The influence of job stress, job satisfaction & organizational commitment towards turnover intention for millennials and generation z employees in internet companies in Indonesia. Jurnal Mantik, 5(4), 2438-2443. [20] Dias, Á., Feixeira, C., Pereira, L., Costa, R. L. D., & Gonçalves, R. (2022). The work-life balance and job satisfaction. International Journal of Services and Operations Management, 43(3), 401-420. [21] Oktaviani, R. (2022). Systematic literature review of job satisfaction: An overview and bibliometric analysis. Jurnal Ekonomi Kreatif dan Manajemen Bisnis Digital, 1(2), 185-203. [22] Achmad, L. I., Noermijati, N., Rofiaty, R., & Irawanto, D. W. (2023). Job satisfaction and employee engagement as mediators of the relationship between talent development and intention to stay in generation Z workers. International Journal of Professional Business Review: Int. J. Prof. Bus. Rev., 8(1), 6. [23] Rudy, R., Widjaja, B. T., & Tecoalu, M. (2023). The effect of job satisfaction and self-efficacy on organizational commitment mediated by organizational culture in generation z age span. Enrichment: Journal of Management, 13(3), 2002-2012. [24] Sagituly, G., & Guo, J. (2023). Job satisfaction and organizational commitment: comparing Generations X and Y. Innovation: The European Journal of Social Science Research, 1-20. [25] Syal, A., Rosnani, T., Daud, I., Kalis, M. C. I., & Hendri, M. I. (2024). The influence of reward, work-life balance on employee retention: The mediating effect of Job satisfaction Generation Z employees in West Kalimantan. Journal of Management Science (JMAS), 7(1), 270-279.
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Naveen R, Dr. Nalini Sunil. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET60022
Publish Date : 2024-04-08
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

