Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Wireless Home Security Using IOT
Authors: G. Sravanthi, Bastepuram Ashok, Chada Sai Cheran Reddy, Anthagiri Lokesh , Kalleda Bhoopesh
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.60040
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
We are living in the fourth industrial revolution. Our life is becoming more comfortable and smarter with the help of rapid upgrade of technology. Internet of things (IOT) is playing a massive role in this. One of the major sides of IOT is a smart Electrical Appliances. As we are in the era of never-ending growth of the internet and its application, smart home system or home automation system is highly increasing to provide comfort in life and improving the quality of life. In this project, we present an IOT based low cost smart electrical equipment automation system. This system is based on a web portal which controlled by an ESP32 WI-FI module. Also, a custom-made private web server is developed for maintaining the current states of electrical devices appliances.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
IR motion detectors are perhaps the most frequently used for security device. Passive IR motion detectors are usually designed to provide an indication to mobile phone as notification or can be an alarm panel in response to detecting IR that is indicative of motion of the object. The alarm panel is responsive to receipt of the breach indication to cause an alarm condition to occur. When a person or motor vehicle enters a monitored area, IR motion detectors are commonly used in conjunction with indoor or outdoor to turn on a light in response to a person moving in the field of view monitored by the motion detector. Someone enters secured places, immediately it will send notification for the Corresponding people. The people can understood something happens in host section. When the owner in remote place, they got messages to the host section by notification and they can view all information of the host section images by mobile phone. A motion detector of an alarm system has a microwave sensor and a passive infrared sensor, and includes signal processing logic for initiating an anti-masking evaluation upon detection of certain conditions. The detector then samples the sensor signals and compares the signals to a series of possible outcomes. Some of the possible outcomes represent the masking conditions, while others represent normal conditions. A match with masking conditions results in an notification or can be alarm signal being generated. An efficient, low power consumption and low cost embedded access control system for Smart home security and remote monitoring[3] based on motion detection is very important for wide range of commercial and security application. Many countries are gradually adopting smart home security control system. Today most of the home and office appliances that we interact with contain microprocessors. All of these appliances have some user interface, but many users become frustrated with the difficulty of using the complex functions of their appliances. We are developing a framework that allows users to interact with appliances through a separate user interface device that they are already carrying. Smart phones are good candidates for providing interfaces because they are common, have communication capabilities to allow connection to appliances, and are already being used for a wide range of different applications. Our framework includes an abstract specification language for describing appliances, a two-way communication protocol, and automatic interface generation software that allows user interfaces to be customized to users and the devices they are using [2]. The most important part of any home security system is accurately detecting visitor who enter and leave through the door. An entrance guard can be managed remotely, detecting visitors at Door and alerting to user via mobile phone is the most natural way to perform security. The proposed system have added features like view video stream through mobile phone [3]. Additionally, voice alert or siren activated to alert neighbors when intruder detected. The system identifies the visitor’s presence, capture and transfers the image through email automatically to home owner to recognize the visitors. The system also generates voice output whenever a person tries to enter into the house. The user can directly login and interact with the embedded device in real time without the need to maintain an additional server. It has a variety of features such as energy efficient, intelligence, low cost, portability and high performance.
A. Background and Motivation:
Internet of Things are the connected physical objects that can transfer the data from one to another without the help of humans. It allows to gather the data from all type of mediums like as kitchen appliances, humans, animals and all type of physical object in which IP address can be enable data transmission over the network by which IOT is embedded with electronics devices such as software, sensor, network in gear. The term IOT and its conception can be traced back to 1985, when Peter T. Lewis spoke about the concept during his speech to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC). The scope of IOT has grown very fast in comparison of other technology. By the help of IOT we can collect real time data and information and also analysis using accurate sensor and internet connectivity that will help in making a beneficial in taking decisions. In recent years, home security has become one of the most important part of life concern. It is necessary to make secure home from the intruders. By the help of sensors (like IR sensor) intrusion detection and surveillance we can easily detect intrusion and raise alert. Smart home security system having the potential that can easily detect the intrusion and having a strong connectivity with the secure environment that contain IR sensor, buzzer to
alert , camera for clicking picture, WIFI module that help in sending messages via notification.
B. Objectives
- Remote Monitoring: Allow homeowners to monitor their homes from anywhere using their smartphones or other devices.
- Real-time Alerts: Notify homeowners of any suspicious activities or breaches in security instantly.
- Integration: Integrate with other smart home devices for comprehensive security solutions.
- Automation: Automate tasks such as locking doors, turning on lights, or activating alarms based on predefined triggers or schedules.
- Scalability: Provide a scalable solution that can be easily expanded or customized according to the homeowner's needs.
- Energy Efficiency: Utilize energy-efficient technologies to minimize power consumption and reduce environmental impact.
- User-Friendly Interface: Offer an intuitive interface for easy setup, configuration, and monitoring by homeowners of all technical levels.
- Privacy and Data Security: Ensure that collected data is kept secure and privacy concerns are addressed effectively.
By addressing these objectives, wireless home security systems using IoT can offer homeowners peace of mind and enhanced protection for their property.

II. RELATED WORKS
Recent advancements in wireless home security leveraging IoT technologies have spurred a plethora of related research endeavors. Scholars have delved into sensor integration, amalgamating various sensors like motion, door/window, and temperature sensors into IoT platforms to fortify home monitoring capabilities. Data fusion techniques have been explored to enhance detection accuracy by amalgamating data from diverse sensors, mitigating false alarms. Machine learning algorithms have been harnessed for anomaly detection and pattern recognition, empowering systems to identify potential threats or irregularities. Remote monitoring and control have emerged as focal points, enabling homeowners to oversee security devices remotely via smartphones or web interfaces. Concurrently, attention has been directed towards ensuring privacy and security, with research probing into privacy-preserving techniques and robust security mechanisms to safeguard transmitted data and ward off cyber threats. Moreover, efforts have been directed towards optimizing energy efficiency in IoT devices and protocols to prolong sensor battery life. Integrating wireless home security systems with existing smart home platforms has also garnered interest, aiming to provide users with a seamless and comprehensive home automation experience. This multifaceted research landscape underscores the evolving nature of wireless home security using IoT, promising further innovation and refinement in the future. In the realm of wireless home security leveraging IoT technologies, a plethora of related research has emerged in recent years, reflecting the growing interest and potential of this domain. One significant avenue of inquiry revolves around sensor integration, where researchers focus on seamlessly integrating various types of sensors, including motion sensors, door/window sensors, and temperature sensors, into IoT platforms. This integration enhances the ability of home security systems to monitor and respond to diverse environmental cues and potential security threats. Additionally, scholars have delved into data fusion techniques, seeking to improve detection accuracy and reduce false alarms by combining data streams from multiple sensors. By employing sophisticated algorithms for data fusion, these systems can better discern genuine security incidents from benign events, thereby enhancing overall reliability. Moreover, machine learning algorithms have become increasingly prevalent in wireless home security research, particularly for tasks such as anomaly detection and pattern recognition. By analyzing patterns in sensor data and user behavior, machine learning models can identify deviations from normal activity and raise alerts for potential security breaches. This capability not only improves the responsiveness of home security systems but also enables them to adapt and learn from evolving threats over time. Another key area of focus is remote monitoring and control, which empowers homeowners to oversee their security systems from anywhere using smartphones or web interfaces. This remote accessibility enhances convenience and peace of mind for users, allowing them to check on their homes and respond to security alerts in real-time, regardless of their physical location. Furthermore, researchers are actively addressing privacy and security concerns inherent in IoT-based home security systems. Efforts are underway to develop robust encryption protocols, authentication mechanisms, and secure communication channels to safeguard sensitive data and protect against potential cyber threats. By prioritizing privacy and security, these advancements aim to foster trust and confidence among users in adopting IoT-enabled home security solutions. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on optimizing energy efficiency in IoT devices and protocols deployed in home security applications. By minimizing energy consumption and extending battery life, these optimizations enhance the sustainability and longevity of wireless home security systems, reducing the need for frequent battery replacements or recharging. Overall, the landscape of wireless home security using IoT is characterized by a multifaceted approach encompassing sensor integration, data analytics, remote accessibility, privacy, security, and energy efficiency. As researchers continue to innovate and refine these technologies, the future holds promising prospects for more robust, intelligent, and user-friendly home security solutions.
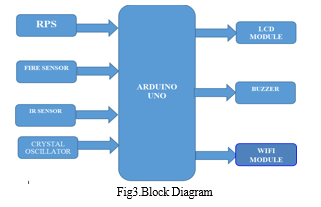
III. METHODS/SOFTWARE
Arduino is an open-source prototyping platform based on easy-to-use hardware and software. Arduino boards are able to read inputs - light on a sensor, a finger on a button, or a Twittermessage - and turn it into an output - activating a motor, turningon an LED, publishing something online. You can tell your board what to do by sending a set of instructions to the microcontroller on the board. To do so you use the Arduino programming language (based on Wiring), and the Arduino Software (IDE), based on Processing. Over the years Arduino has been the brain of thousands of projects, from everyday objects to complex scientific instruments. A worldwide community of makers students, hobbyists, artists, programmers, and professionals has gathered around this open-source platform, their contributions have added up to an incredible amount of accessible knowledge that can be of great help to novices and experts alike. Arduino was born at the Ivrea Interaction Design Institute as an easy tool for fast prototyping, aimed at students without a background in electronics and programming. As soon as it reached a wider community, the Arduino board started changing to adapt to new needs and challenges, differentiating its offer from simple 8-bit boards to products for IoT applications, wearable, 3D printing, and embedded environments. All Arduino boards are completely open- source, empowering users to build them independently and eventually adapt them to their particular needs. The software, too, is open- source, and it is growing through the contributions of users worldwide.
A. Why Arduino?
Thanks to its simple and accessible user experience, Arduino has been used in thousands of different projects and applications. The Arduino software is easy-to-use for beginners, yet flexible enough for advanced users. It runs on Mac, Windows, and Linux. Teachers and students use it to build low cost scientific instruments, to prove chemistry and physics principles, or to get started with programming and robotics. Designers and architects build interactive prototypes, musicians and artists use it for installations and to experiment with new musical instruments. Makers, of course,use it to build many of the projects exhibited at the Maker Faire, for example. Arduino is a key tool to learn new things. Anyone - children, hobbyists, artists, programmers - can start tinkering just following the step by step instructions of a kit, or sharing ideas online with other members of the Arduino community. There are many other microcontrolers and microcontroller platforms available for physical computing. Parallax Basic Stamp, Net media's BX-24, Phidgets, MIT's Handyboard, and many others offer similar functionality. All of these tools take the messy details of microcontroller programming and wrap it up in an easy-to-use package. Arduino also simplifies the process of working with microcontrollers, but it offers some advantage for teachers, students, and interested amateurs over other systems:
- Inexpensive: Arduino boards are relatively inexpensive compared to other microcontroller platforms. The least expensive version of the Arduino module can be assembled by hand, and even the pre-assembled Arduino modules cost less than$50
- Cross-platform: The Arduino Software (IDE) runs on Windows, Macintosh OSX, and Linux operating systems. Most microcontroller systems are limited to Windows.
- Simple, Clear Programming Environment: The Arduino Software (IDE) is easy-to-use for beginners, yet flexible enough for advanced users to take advantage of as well. For teachers, it's conveniently based on the Processing programming environment, so students learning to program in that environment will be familiar with how the Arduino IDE works.
- Open Source and Extensible Software: The Arduino software is published as open source tools, available for extension by experienced programmers. The language can be expanded through C++ libraries, and people wanting to understand the technical details can make the leap from Arduino to the AVR C programming language on which it's based. Similarly, you can add AVR-C code directly into your Arduino programs if you
- Open source and Extensible Hardware: The plans of the Arduino boards are published under a Creative Commons license, so experienced circuit designers can make their own version of the module, extending it and improving it. Even relativelyin experienced users can build the breadboard version
B. MC Programming Language: Embedded C -
This is the most widely used programming language for embedded processors/controllers. Assembly is also used but mainly to implement those points of the code where very high timing accuracy, code size efficiency, etc. are prime requirements. Embedded C is perhaps the most popular languages among Embedded Programmers for programming Embedded Systems. There are many popular programming languages like Assembly, BASIC, C++ etc. that are often used for developing Embedded Systems but Embedded C remains popular due to its efficiency, less development time and portability. An Embedded System can be best described as a system which has both the hardware and software and is designed to do a specific task.
Some examples of the embedded systems in a modern-age car are Anti-lock Braking System (ABS), Temperature Monitoring System, Automatic Climate Control, Tire Pressure Monitoring System, Engine Oil Level Monitor, etc.
Embedded Systems consists of both hardware and software. If we consider a simple Embedded System, the primary hardware module is the Processor. The Processor is the heart of the Embedded System and it can be anything like a Microprocessor, Microcontroller, DSP, CPLD (Complex Programmable Logic Device) or an FPGA (Field Programmable Gated Array). All these devices have one thing in common: they are programmable i.e., we can write a program (which is the software part of the Embedded System) to define how the device actually works.
C. Moving On
Connect your Arduino to the computer with the USB cable. You do not need the battery for now. The green PWR LEDwill light. If there was already a program burned into the Arduino, it will run.Start the Arduino development environment. In Arduino-speak, programs are called “sketches”, but here we will just call them programs.In the editing window that comes up, enter the following program, paying attention to where semi- colons appear at the end of command lines.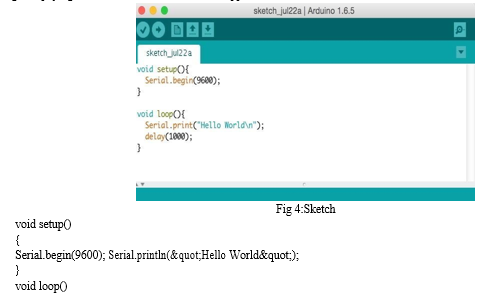
IV. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Implementing IoT in wireless home security systems has ushered in a new era of convenience, efficiency, and enhanced protection for homeowners. The integration of IoT technology has fundamentally transformed traditional security systems by leveraging the power of wireless connectivity, smart sensors, and data analytics to create comprehensive and intelligent security solutions.
One of the most significant results of incorporating IoT into home security is the seamless connectivity it offers. With IoT-enabled devices, homeowners can remotely monitor their properties in real-time, receiving instant alerts on their smartphones or other connected devices in the event of suspicious activities or security breaches. This level of connectivity ensures that individuals stay informed and can take immediate action to address any potential threats, regardless of their location.
Furthermore, the customization and integration capabilities of IoT-based systems provide homeowners with a tailored security solution that can be adapted to suit their specific needs and preferences. These systems can seamlessly integrate with other smart home devices, such as smart locks, lights, and cameras, allowing for a comprehensive home automation and security ecosystem. This integration not only enhances convenience but also enables a more cohesive and effective approach to home security.
The efficiency of wireless connectivity in IoT-based security systems also cannot be overstated. By eliminating the need for complex wiring, installation becomes faster, easier, and less invasive. Additionally, IoT-enabled systems can optimize energy usage and reduce false alarms through advanced algorithms and machine learning, ensuring a reliable and efficient security solution that minimizes unnecessary disruptions and energy consumption.
Remote management capabilities further enhance the convenience and accessibility of IoT-based home security systems. Homeowners can remotely arm or disarm their security systems, check live camera feeds, and review past events from anywhere with an internet connection. This level of control not only provides peace of mind but also allows individuals to stay connected and informed about the security status of their homes at all times.
Moreover, the scalability of IoT-based security systems enables easy expansion or adjustment to accommodate changes in the home environment. Whether adding additional sensors, expanding coverage areas, or integrating new devices, homeowners can seamlessly adapt their security systems to meet evolving needs and preferences without requiring extensive reconfiguration or installation efforts.
Finally, the data analytics capabilities of IoT devices play a crucial role in enhancing home security. By analyzing collected data for patterns, trends, and potential vulnerabilities, homeowners can gain valuable insights into their home's security status and take proactive measures to mitigate risks and improve overall security posture. This data-driven approach enables continuous optimization and enhancement of the security system, ensuring that it remains effective and up-to- date in the face of evolving threats and challenges.
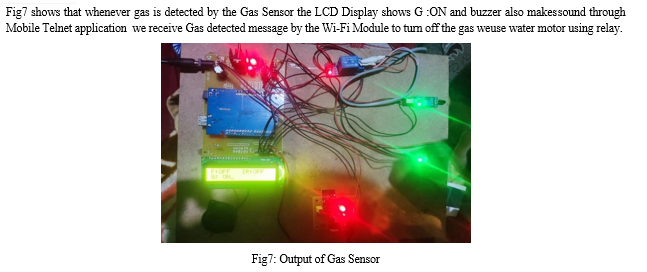
Fig5 shows that whenever an object is detected by the IR Sensor the LCD Display shows IR :ON and buzzer also makes sound through Mobile Telnet application we receive Object detected message by the Wi-Fi Module.

VI. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Sincere thanks of gratitude are extended to the Guide “G. Sravanthi”, Assistant Professor and to coordinator “Dr. Sudha Arvind”, Associate Professor, Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, for their guidance and support in completing the project and also to “Dr. G. Srikanth”, Professor and Head, of the Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, and “Dr. A. Raji Reddy” Director of CMR Technical Campus for providing all the facility that was required.
Conclusion
There are some future works can be done by adding some of the artificial intelligence technique into the smart home system such as the system can automatically deal with the cases happening in the home. For instance, the system can determine the seriousness of some cases such as thieve intrusion by automatically report to the police station and notify the user. Moreover, the system also can be added with CCTV to strengthen the security part of this project. In this project we have a large scope to develop and working with this project. We try to listed some tasks which would be added in future Add a special camera and using image processing try to find out known and unknown face. If detect known face system can send SMS and email with picture and information about this face which is store in previous. We can make the web application more users friendly. Can be added voice commands technology.
References
[1] Andrea Z and Lorenzo V., “Internet of Things for Smart Cities,” IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol/issue: 1(1), Feb 2022. [2] Isna K. and S. D. Sawant, “Integration of Cloud Computing and Internet of Things,” International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer and Communication Engineering,vol/issue: 5(4), Apr 2016. [3] Sonali D. T., “Cloud Computing and Software-Based Internet of Things,” International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering, vol/issue: 6(4), Apr2014. [4] Jonathan K., “Using Active Queue Management to Assist IOT Application Flows in Home Broad band Networks,” 2017 IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol/issue: 4(5), Oct 2017. [5] Pengfie Z., et al., “Secure Location of Things(SLOT) : Mitigating Local Spoofing Attacks in Internet of Things,” IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 4, Dec 2017. [6] Akriti S., et al., “Intelligent Accident Management System using IoT and Cloud Computing,” 2nd International Conference on Next Generation Computing Technologies, Oct 2016. [7] C. Chatrapathi and N. R. Venkatesakumar, “VANET based Integrated Framework for Smart Accident Management System,” International Conference on Soft- Computing and Network Security, Feb 2015. [8] Priyal R. and Vanthana S., “Car Accident Notification Systembased on Internet of Things,” International Journal of Computer Applications, vol/issue: 107(17), Dec 2014. [9] H. M. Ali and Z. S. Alwan, “Car Accident Detection and Notification System Using Smartphone,” International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing, vol/issue: 4(4), pp. 620-635, Apr 2015. [10] S. R., et al., “An IoT Based Accident Prevention and Tracking System for Night Drivers,” International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering, vol/issue: 3(4), Apr 2015
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 G. Sravanthi, Bastepuram Ashok, Chada Sai Cheran Reddy, Anthagiri Lokesh , Kalleda Bhoopesh . This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET60040
Publish Date : 2024-04-09
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

