Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
A Study on Wireless: Overviews of Mobile Security and Privacy
Authors: Rakesh Kumar
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.63726
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Background: Computer networks have become a very important and essential part of our daily life due to wireless Smartphone, it has become easy to communicate or share data through various technologies like wired or wireless. Generally there has been reliance on wireless technology due to various advantages like ease of installation, mobility, reconfiguration, low infrastructure cost, ability to storage, banking transactions, confidential data exchange etc., but Due to the wireless channel being in the air or open, one has to face more attacks like Phishing, Spyware, Botnet, Trojan, Worm, Spam, etc. In this paper, we will discuss different types of malware and also discuss the basic steps to avoid malware. Smartphone has become an important support in our daily life due to its wireless communication and seamless connectivity and being a small electronic device. Due to storage in Smartphone, we keep personal data and financial data. To ensure that no one misuses this data, we do research and collect information. Objective: To study the attack on Smartphone through wireless communication and to suggest protection against this attack and to make people aware so that this dangerous attack can be avoided. Apart from this it is to be said that computer programming and research is always done for the society. Methodology: I decided to collect data from secondary sources. We performed a literature review based on a combination of the keywords \"mobile security,\" \"threat,\" \"Smartphone\" and \"malware,\" in an electronic search with Google web search engine and Google Scholar. Result: In this research paper, we have suggested the first aid to avoid the attack, how the attack can be avoided. Conclusion: There is always an arms race between attackers and defenders in wireless Smartphone data communications. A deeper study reveals that security and attack are a cyclical process between attackers and defenders, to which common users will continue to fall victim.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, all human beings have become dependent on their Smartphone; there are two main reasons for this: The first reason is that being a wireless and small device, this device can be easily kept in the packet; there is no need to bring and carry it to any place. One does not have to face any problem, everyone tries to solve most of the tasks from their Smartphone, and some of the major tasks done from the Smartphone are as follows: (1) Money transactions with the help of Smartphone, (2) Secret data exchange, (3) Keeping secret data in storage, (4) Email login in Smartphone, (5) Online shopping applications, (6) Operating office through WhatsApp, (7) Communicating quickly with all relatives, (8) Viewing train running information and booking railway reservation tickets, (9) Social media sites, (10) Studying online, (11) Songs and Watching movies, (12) Games, (13) Dictionary, (14) Reels are made, (15) Play YouTube and also upload their videos, (16) Business, etc [1].
Recent years have shown a significant increase in the popularity and ubiquity of mobile devices among users all around the globe [2]. Smartphone is a device that almost everyone has and everyone is using all the time; now the problem is that the users' Smartphone are not safe. Because Smartphone attackers have created many malware and viruses to collect money, through which hackers attack Smartphone and demand money.
A Smartphone is considered a personal device; While using it, there is a possibility of malware coming in through three types of mediums: The first medium is when you are doing any work by connecting to the internet; Second, when you are connected to the network and doing some work and third, when you are exchanging data from the pendrive [3].
If any person or any component is capable of collecting and storing personal data, then no researcher and developer can ensure that this data is not collected and misused by anyone. But it is necessary to be sure about all types of privacy and data security in smart phones.
Mobile communication systems are exposed to a variety of frauds that are commonly found in communication channels and mobile devices. These vulnerabilities can be the result of inadequate technical controls, but they can also result from the poor security practices of consumers.
However, security controls are not always applied consistently on mobile devices, and it is unclear whether consumers are aware of the importance of enabling security controls on their devices and adopting recommended practices. The user can also be the main reason for an attack on a Smartphone. Because due to his unknowing mistake, his Smartphone gets attacked, due to which he has to face huge loss in his financial condition. Many Smartphone users are not fully aware of which security practices to use.
Mobile devices may contain malware: Consumers may download applications that contain malware. Consumers download malware unknowingly because it can be disguised as a game, security patch, utility, or other useful application. It is difficult for users to tell the difference between a legitimate application and one containing malware.
For example, an application could be repackaged with malware and a consumer could inadvertently download it onto a mobile device.
These applications are officially distributed via online stores referred to as app markets — Apple App Store for the iOS platform and Google Play Store for the Android platform. These markets provide a convenient venue for app developers to distribute their apps and for users to explore and download new apps. This has driven the tremendous development rate of apps in recent years.
Users who see their device as a Smartphone have greater security awareness than users who see their devices just as a phone. Users who see their device as a Smartphone feel less secure as users who see their device just as a phone.
A. Paper Organization
This paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presented the malware analysis and detection approaches taxonomy. 3 presented the Smartphone and Communication security. In Section 4 this paper discussed the recent review papers. In Section 5, the research methodology that is followed is presented. In Section 6, we have presented the Result. In Section 7, we have presented the Conclusion.
RQ1: How many types of malware are there in wireless mobile communication system and how does it attack?
RQ2: How are security treatments used in wireless communication systems for security?
RQ3: Which authentication
II. SMARTPHONE SECURITY THREATS
Smart phones are quickly approaching PC capabilities, and the same incentives exist for hackers: frauds, stealing personal and business information, and extortion—hackers are poised for the attack, with many different avenues available to spread malware [4].
The following brief review of smart phone malware shows that the malicious capabilities of hackers have been clearly demonstrated; these are just some of the malware threats listed in the report by Mobile Iron.
A. Malicious App
Malicious apps are specially designed to attack Smartphone systems. These malware apps significantly relay on the exploitation of OS and software technology of Smartphone. We can enlist the malicious apps into the following four categories: [5]
|
S.N |
Malware |
Description |
|
2.1.1 |
Phishing |
Smartphone attackers collect personal account details and credit card details and debit card details from Smartphone users through credentials, email or SMS, which are impersonated as genuine. |
|
2.1.2 |
Spyware |
Smartphone users' activities are being monitored, which means that personal information is being extracted or inferred from the Smartphone. Compared to a surveillance attack, spyware does not have specific target victims. |
|
2.1.3 |
Botnet |
A botnet is a set of zombie devices infected with malware so that a hacker can take control of them remotely and give them remote control. |
|
2.1.4 |
Trojan |
When a user runs the trusted executable files that contain the harmful instructions (Trojan), the Trojan is triggered. Trojan can be used to steal data, disable some mobile device features, and allow an attacker to install other malware. |
|
2.1.5 |
Worm: |
A worm is a malware and a type of attacker's weapon that replicates itself, usually without user intervention, to spread from one device to another using various means through existing networks. |
|
2.1.6 |
Spam: |
Spam is any type of unsolicited, unsolicited digital communication that is sent in bulk. Spam is often sent via email, but can also be distributed via text messages, phone calls or social media. |
|
2.1.7 |
Hidden Process |
These are the applications in which some anonymous activities are embedded without providing any knowledge to the users. For example, a gaming application scans for the nearby wireless devices which are not necessary for any of the gaming functionalities. These types of hidden operations can harm users and user experience. |
Table 01: malware
- Phishing: The main platform for phishing attacks is spam emails, which are sent out in mass quantities by cybercriminals. Recently, we have witnessed a new form of phishing, which is using SMS text messaging (so-called ?smashing?) to send a fraudulent link to a mobile device. Social media are also used by hackers to take advantage of mobile phone users. This type of attack is aimed at users directly, most frequently exploiting human psychology rather than using technical hacking techniques. This aims to [6] Phishing attacks Smartphone just as much as it does desktop platforms. In fact, many users trust their mobile devices more than their computers, this is user error. And thus are more vulnerable to phishing. Mobile phishing comes across as particularly attractive because wireless communications enable phishing not only via e-mail, as is the case with PCs. Social media phishing is becoming a bigger issue as social networking sites contain increasing amounts of personal information that phishes can use to make their attacks more effective.
- Spyware: Hackers can use spyware available online to hijack a phone, allowing them to hear calls, see text messages and e-mails, and even track a user’s location through GPS updates. Most commercial mobile spyware applications send an update of captured communications or location data to a website where the spy logs in to view the data. In some cases, SMS communications inform the spy that the system has obtained new data. The software can even create a hidden access point inside a mobile phone that lets a hacker turn on the device without it ringing [7].
- Botnet: Attackers create a botnet by infecting multiple machines with malware programs, which victims typically obtain through e-mail attachments or from compromised applications or websites. Malware gives hackers remote control of "zombie" devices, which can then be instructed to perform harmful actions, such as locking files, slowing down mobile phones, increasing Internet usage, stealing personal data, financial. Stealing ID & Password gives remote control. The easiest way for an attacker to profit from a mobile zombie network is to send SMS or Multimedia Message Service (MMS) communications to a premium phone account that charges victims per message. Scammers act as affiliates of the premium account owner, and receive some of the money generated from their attacks [8].
- Trojan: Trojans are specially crafted malware programs that are designed to look like interesting packages (for example, games, system updates, or utilities), or copies of legitimate programs that have been repackaged to include harmful elements, or has been trojaned. It comes in the form of antivirus, it comes in the form of speed booster, and it comes in the form of promotion. After the arrival of the smartphone, the entire system shuts down, due to which a factory reset is required and ultimately the data gets lost [8].
- Worm: A worm can damage and compromise the security of Smartphone. Moreover, it duplicates itself, typically propagating from one device to another, using different means through an existing network without the users’ intervention. In fact, worms can be easily spread by just one click to infect Smartphone in any part of the world with a large chance of success. Moreover, as network function virtualization will be introduced into next generation mobile networks to reduce capital and operating expenditures [9], worm-based attacks to the virtualization environment and hence to Smartphone are expected to increase.
- Spam: That is, sending unwanted messages or advertisements to people is called spam. If you use the Internet, you too must have to deal with spam messages and promotional emails. But we need to be more careful about viruses and credit card fraud.
- Hidden Process: These are the applications in which some anonymous activities are embedded without providing any knowledge to the users. For example, a gaming application scans for the nearby wireless device which is not necessary for any of the gaming functionalities. These types of hidden operations can harm users and user experience.
B. Malware Downloader
A malware downloader (i.e. trojan downloader) is a harmful application, basically installed by an exploit or some other fraudulent causes like an email attachment or a downloaded image that triggers to install the malicious program onto a victim’s computer [10].
C. Fake Operation
Android OS family is very diverse. There are numerous official as well as unofficial versions of this OS. This open nature of the platform has given the attackers to introduce various fake operations. Faking operator’s identity, model, version, software update as well as fake apps’ goal, etc are some common examples of fake operations.
D. Hidden Das
”It won’t hurt if you don’t know it.” is a common proverb but unfortunately, this phase isn’t suitable for today’s Smartphone security risks. Many of the free apps contain excessive ads that are available in the app store. That is legal because they acknowledge both parties that the app contains ads. But some malicious app contains hidden ads that may be harmful to users. Often these apps cause slowing down the device, sucking mobile data, draining the battery and so on. A recent study has shown that more than 5000 apps of both the major Smartphone platforms contain hidden apps. It also causes a huge amount of loss to the advertising organization. They lose about $85 million per year because of the hidden ads [11,12].
E. Premium Text
Sometime we may receive some messages from a four or five digit phone numbers e.g., get jokes for USD1 per month or send STOP to cancel the service. Majority of the users may not activate the service so they are not concern about it but after a month they get a bill of USD1. This unintentional or fake registration to a service is done by some scammers and fraudsters. They sign up for the victim by using the victim’s phone number from some websites [13, 14].
III. SECURITY SYSTEM SMARTPHONE AND COMMUNICATION
Wireless Smartphone security and privacy systems depend on user usage. Pattern and Awareness: This includes the principles and efforts taken by the developer regarding security and privacy. This area is very important to ensure security and privacy.
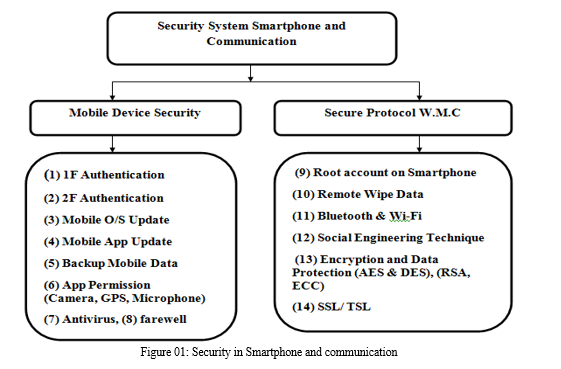
A. Mobile Device Security
In wireless mobile communication systems, mobile device security is crucial to ensuring the availability, confidentiality, and integrity of data. By establishing a trusted and secure state during device startup and assuring the execution of trusted software and firmware, secure device bootstrapping techniques, such as secure boot procedures and integrity checks prohibit unauthorized modifications. Mobile application vulnerabilities are reduced significantly by using secure application development and deployment techniques. Potential security risks can be reduced by adhering to secure coding practices, carrying out thorough security testing, and following secure coding principles. App vetting processes, code signing, and sandboxing techniques employed by application stores and marketplaces verify the authenticity and integrity of applications before they reach users. Mobile malware detection and prevention mechanisms are vital for safeguarding mobile devices and wireless communication.
- 1F authentication/ one steps Verification: 1F (one factor) authentication means that the app and website are locked with ID and password. A security gap was found in this lock due to which hackers were successful in hacking. The problem with this was that after knowing something, the hacker would take control.
- 2F authentication/ Two Steps Verification: 2f authentication means that OTP has been used along with ID & password to lock apps and websites. If the Smartphone attacker somehow gets to know the ID and password, then OTP will be required. This is advantage of 2F authentication/ Two Steps Verification.
Example: In the net banking website of State Bank of India, two steps verification is used: in the first step, enter ID & password and in the second step, enter one time password.
|
Level of authentication ( Example of yono SBI app |
||
|
S.N |
Lock Type |
Discretion |
|
1 |
Screen Lock |
Almost one-third of the total users don’t concern about the lock-screen security and they use the traditional swipe-to-unlock method [36]. Though it helps to protect the phone from accidental touches when the phone is in the pocket but the phone cannot provide any security barrier if the phone got stolen or compromised somehow. All type of Android smartphone offer PIN, password, and pattern (mostly) to secure the phone which can easily be enabled from the security options in the settings. Additionally, modern smartphones have been introducing biometric sensors like fingerprint sensor, iris, and faceID to enhance smartphone security. Among these multiple biometric-based methods, fingerprint-based biometrics is the most secure way to date. |
|
2 |
App Lock |
App Lock is a feature in mobile security for smartphones that protects your sensitive apps with a PIN, pattern or fingerprint. App locking requires you to enable usage access permission in your device's security settings. |
|
3 |
User ID & Password/ Mpin |
Thousands of smartphone users use easy passwords like 123456, phone number, birth date, and so on to remember it which is very simple to guess for an attacker. So, selecting passwords, especially for online accounts, should not be that much simple and straightforward job. A user should not use a single password to handle all his/her accounts because compromising one account’s password can led compromise all other accounts of that user. To minimize the vulnerabilities, the selection of passwords must be based on some criteria. For example, every person should make his/her own reasoning for each password so that every time he/she can put it by remembering the reasoning developed earlier. Additionally, using two-step verification can add extra strength to an account; even if an intruder or hacker achieves the password of a particular account, he/she can’t access it without compromising the two-factor authentication media such as cell phone or email account configured earlier for the verification system. So, all the passwords including lock-screen password/PIN, Google accounts, Facebook, Twitter and so on should be selected wisely in order to remember and protect them easily. |
Table 02: Level of authentication
3. Mobile O/S Update: From the security point of view of Smartphone operating system, the developer keeps providing updates from time to time so that if there is any kind of virus in the mobile, it eliminates it and does not allow the virus to enter. Google Inc. and other manufacturers provide system updates which include security patches, features and functionalities, UI improvements and so on to overcome vulnerabilities and to ensure smoother user experience. To get the finest user experiences, it is definitely a good idea to update the phone software regularly. The newest versions of the software help the users to run their phones more smoothly and quickly with minimum numbers of lags and security vulnerabilities.
4. Mobile App Update: Smart phone app developers keep updating the app from time to time and the user should keep updating it so that he can avoid the danger. In this situation, sometimes the problem of app repack also occurs due to which malicious programs can also be introduced. Android OS is getting better in terms of security enhancement day by day. From Android v6.0, runtime permission request is added. It means the user needs to agree with critical permission(s) during app usage. Though this process is safer than the previous versions’ of agreement, people often make mistakes while opening the app for the first time: they often grant permissions without reading and knowing the consequences of it. They also do not check the list of permissions during apps installation. Instead, they just accept the requests without thinking about the consequences. It may be harmful because the developer could take advantages of it.
5. Backup Mobile Data online: We keep a lot of data in Smartphone, it also contains important data, and hence arrangements for online backup have been made. This has been done so that in case the data gets lost or corrupted, there will be no regrets.
6. App Permission (Camera GPS Microphone): There is no need to give more permissions than required while installing an app in a Smartphone. There is a possibility of danger if there is more permission given than required. Like Camera GPS, Microphone. Android OS is getting better in terms of security enhancement day by day. From Android v6.0, runtime permission request is added. It means the user needs to agree with critical permission(s) during app usage. Though this process is safer than the previous versions’ of agreement, people often make mistakes while opening the app for the first time: they often grant permissions without reading and knowing the consequences of it. They also do not check the list of permissions during apps installation. Instead, they just accept the requests without thinking about the consequences. It may be harmful because the developer could take advantages of it.
7. Antivirus: Antivirus is a computer program or software that has the ability to escape from the virus, but the antivirus must be safe and secure.
8. Smartphone Farewell: Farewell has the ability to control security, it has the option of on/off, and the user can turn it on/off as per his knowledge and requirement. There is permission for danger to come or not to come.
B. Secure Protocols for Wireless Mobile Communication
In wireless mobile communication systems, secure protocols are essential for creating secure communication channels, preserving data integrity, and guaranteeing secrecy. SSL/TLS is a collection of protocols that is often used and allows for secure communications between clients and servers when using the internet. To ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of transmitted data, SSL/TLS protocols use a combination of symmetric and asymmetric encryption algorithms, digital certificates, and secure key exchange mechanisms.
- Root Account on Smartphone Storage: To root a device is to obtain super user access on an android device. This is similar to jail breaking an Apple device. When you purchase a Smartphone, for example, the manufacturer and/or carrier place limitations on the device to help protect them from malware and from users unintentionally damaging the device.
- Remote Wipe Data: Remote wipe is a security feature that allows a network administrator or device owner to send a command that remotely deletes data from a computing device. It's primarily used to erase data on a device that has been lost or stolen, so the data won't be compromised if it falls into the wrong hands. Encrypting the data of a Smartphone can help to improve users’ security and privacy one step ahead. A user can only get access to the encrypted data with a valid password or key. Encryption of a Smartphone enables the needs for a password or key in every boot up of the Smartphone. Apart from that, it doesn’t change anything how a user uses his/her Smartphone. From Android version 6.0, data encryption is enabled by default. Encryption may cause slowing down the performance of some older Smartphone, but it doesn’t affect today’s Android devices. If an application does not meet certain challenges, it should not be installed on phone. Anti-virus provider Kaspersky lab published a report that an IT-based company developed an app called “skygofree” which was released with 48 different commands that was able to risk a user’s safety in several ways like it relies on 5 different exploits to achieve root privilege which allows it to bypass security key and it was also capable of location-based recording, capturing image, videos, calendar data and other personal information [13].
- Bluetooth & Wi-Fi: Minimizing both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi usage reduces exposure to having vulnerabilities exploited, although the flaws are not in these standards, but in their implementations. Here, it should be noticed that the disabling action requires an intentional interaction from a user. However, there are tools (e.g., Auto Bluetooth) that turn Bluetooth on or off without any user interaction, based on the rules defined by a user.
- Social Engineering Technique: Social engineering is a term that encompasses a broad spectrum of malicious activity such as phishing, pretesting, baiting, quid pro quo, and tailgating (?piggybacking?). With this human-centric focus in mind, it is up to a user to be aware of malicious ?actors? who engage in social engineering attacks hunting for human greed and ignorance [14]. Organizations, in particular security analysts, might also consider conducting social engineering penetration tests (also known as social pen testing) among employees. By design, social pen testing is the practice of applying social engineering scams on an organization’s employees to evaluate their capability to provide sensitive information. Such an assessment is beneficial by providing a real attestation on the level of adherence to the company’s security policies by particular individuals. 3.13. Encryption and Data Protection (AES & DES), (RSA, ECC):
- SSL/ TSL: In wireless mobile communication systems, secure protocols are essential for creating secure communication channels, preserving data integrity, and guaranteeing secrecy. SSL/TLS is a collection of protocols that is often used and allows for secure communications between clients and servers when using the internet. To ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of transmitted data, SSL/TLS protocols use a combination of symmetric and asymmetric encryption algorithms, digital certificates, and secure key exchange mechanisms.
IV. LITERATURE REVIEW
- N. Leavitt (2011), suggested that there are two primary attack vectors for mobile phones. The first is when a mobile phone connects the internet; the second is when a mobile phone connects to a network. Because too much individual and financial data is being stored on a phone, this is making the mobile phone environment more and more appealing to hackers. 2010 saw a 46% boost in mobile phone security, according to McAfee Labs, and every day, more than fifty five thousands (55,000) new mobile malware variants are discovered there [15]. While PCs are increasingly being used to establish mobile botnets, the main goal of mobile malware is to steal money and personal information. Similar to the emergence of android botnets, this issue has been a topic of discussion for the past year [16]. Due to the mobile nature of smart-phones, the aforementioned blogger, Marko, properly compares the concept of an Android botnet to a salesman who is on the road and infected with tuberculosis.
- Mario Ballano (2011) , a Symantec researcher, claimed to have discovered a new attack method for Android that is comparable to Windows DLL hijacking [17]. This is more of vulnerability in some apps that dynamically load code utilizing the Android classes Public Constructors and DexClassLoader than it is an OS flaw. Ballano claimed that the few apps that he found to be susceptible to this technique have been reported to Google. As of November 2012, Google's response to the issue is unknown, and a patch has not yet been released. Another attack method for Android phones is fake online "Google Play" stores. Tim Wyatt, a software engineer at Lookout, informs us that GGtracker Trojan-infected software distributed through fake online shops has the ability to sign up users for premium SMS services without their consent or even informing them that a transaction has taken place.
- Khan et al. (2015) researched several security-related difficulties, risks, and vulnerabilities for mobile users [18]. Their analysis includes a number of different mobile dangers, including physical threats, application-based threats, network-based threats, and web-based threats. One issue involving earnest money and mobile weaknesses is a botnet. They claim that biometric authentication is a key security defense mechanism for mobile security and data privacy. Every phase of developing a mobile application must include security mechanisms.
- Cifuentes et al.(2015) conducted an analysis of the flaws discovered in health-related mobile applications [19]. In order to identify vulnerabilities, they divided mobile health apps into six groups depending on the functionalities of the apps and downloaded 10 Android apps from the Google Play store for each group. 60 m-Health apps have 157 vulnerabilities in total. According to their findings, the majority of vulnerabilities and high-risk levels are present in apps with remote monitoring capabilities. Their findings indicate that 64% of the flaws in m-Health apps linked to unreliable input.
- Chatzikonstantinou et al.(2016), revealed cryptographic vulnerabilities in mobile applications and categorized as fragile cryptographic algorithms, weak cryptographic keys, and feeble implementation of cryptographic methods, and weak parameters [20]. They manually conducted static and dynamic analyses on 49 arbitrary Android apps that they downloaded from the Google Play store. According to their findings, 12.2% of Android apps have no cryptographic methods at all, while nearly 87.8% of Android apps use weak cryptographic algorithms.
- Shukla et al. (2015) A new key concord and authentication procedure for Electronic Health Record systems was put into place [21]. Since the EHR system has a variety of users, including doctors, lab workers, patients, and insurance agencies, adequate key agreements and authentication are essential. The suggested protocol operates on a commitment system and will halt communication if authentication is unsuccessful. They claimed that the binding/hiding aspect of the protocol makes Man in the Middle attacks particularly difficult to execute in wireless communications.
- According to Choo (2014), advancements in new technology and advancements in security measures must happen simultaneously [22]. According to the routine activity idea, criminal activity happens when there is a motivated attacker, a targeted gadget, and a weak guardianship. The ability of cloud storage applications like DropBox, Google Drive, One Drive, etc. to hold a sizable amount of user data makes them popular targets for attackers. They looked at celebrity iCloud accounts that had been compromised and found that the majority of hacks target specific security questions, usernames, and passwords.
- According to Agasi (2015), there isn't a perfect way to prevent issues with mobile security. Implementing appropriate security rules, incorporating current security, and protecting data on mobile devices are the key concerns with mobile security [23]. Corporates must build a secure environment for mobile devices, threat management, and security rules that are independent of the devices and operating systems used in them in order to secure company documents and data.
- Cheng et al. (2007) proposed a virus detection and alert system for smart-phones. by. It identifies viruses by gathering activity data from the smart phones and doing joint analysis to identify odd behaviors on both a single device and the entire system. When a potential infection is identified, they employ a proxy to offload the processing load from resource-constrained smartphones, and the proxy delivers targeted alerts to infected devices and a fraction of the uninfected devices to stop the spread. The scientists asserted that the approach can successfully stop widespread viral outbreaks while requiring minimal overhead. In order to improve security perception, this study offers a useful mobile technology-based learning approach that puts the needs of the students first. The strategy outlines the creation of a modular mobile security software that addresses both established and new security concerns and threats. This strategy offers students a practical and efficient way to improve the security of their devices as using smart devices is increasingly becoming a part of their daily routines [24].
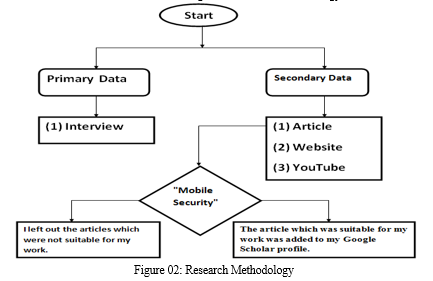
V. METHODOLOGY
We followed the methodology which is shown in Figure 1 to introduce this paper. Firstly, we focused on the review papers that have been written recently to identify the limitations of the existing reviews and then show the need for new literature review papers. Secondly, in addition to the review papers, we used specific key words to collect the relevant experimental papers. Thirdly, according to the analysis and the detection approaches along with the extraction and the representation methods that have been utilized in each single study, the literature review is classified. Four processes, which are reading, understanding, comparing, and criticizing, have been conducted in the last phase to obtain the final results of this survey and highlight the future directions and open issues in the malware detection and classification area. Figure 2 shows the methodology that is followed to write this survey.
Conclusion
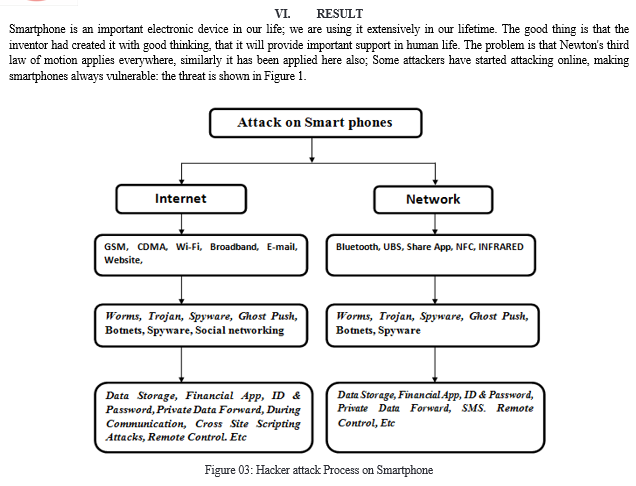
In wireless mobile communication system, there are four types of attacks; Smartphone users are vulnerable to threats: the first occurs when an attacker connects via the Internet, the second occurs when someone connects via a network; The third occurs when the smart phone is lost or stolen; the fourth occurs when data is transferred from the pendrive. There seems to be a notable lack of material on smartphone security, particularly when it comes to morphine and botnet security. The volume of articles written has increased greatly, although not as much as might have been anticipated given the increase in mobile smart-phone usage globally. Last but not least, Android security problems have not been clearly resolved, leaving room for further scientific investigation of malware attacks. Security device manufacturers agree that protecting the entire spectrum of goods is very challenging because the risks are dispersed and not concentrated in one area. They suggest some standard precautions to avoid security lapses. There is a need for intensive research related to the security of mobile storage and communications.
References
[1] IDC, “Worldwide Smartphone Shipments Top One Billion Units for the First Time, According to IDC,” press release, 27 Jan. 2014; https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp? containerId=prUS24645514 [1] IDC, “Worldwide Smartphone Shipments Top One Billion Units for the First Time, According to IDC,” press release, 27 Jan. 2014; https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp? containerId=prUS24645514 [2] Statista, Smartphones—Statistics & Facts, Statista, Hamburg, Germany, 2020, https://www.statista.com/topics/840/ smartphones/. [3] A. Papageorgiou, M. Strigkos, E. Politou, E. Alepis, A. Solanas, and C. Patsakis, “Security and privacy analysis of mobile health applications: the alarming state of practice,” IEEE Access, vol. 6, pp. 9390–9403, 2018. Malware [1] Top 7 Mobile Security ?reats in 2020, https://usa.kaspersky. com/resource center/threats/top-seven-mobile-security-threatssmart- phones-tablets-and-mobile-internet-devices-what-the-fu ture-has-in-store, 2020. [2] New MobileIron Report Details Most Common Mobile ?reats and Blacklisted Apps, https://www.techrepublic.com/ article/new-mobileiron-report-details-most-common-mobilethreats- and-blacklisted-apps/last, 2020. [3] A. Harkness, “Mobile malware threats,” 2019, https://www. netmotionsoftware.com/blog/security/mobile-malware-threats. [4] Veracode, ”Details on malicious mobile application security,” [Online], Available: https://www.veracode.com/security/rise-malicious-mobile-applications, Accessed: 2 Apr 2019, 2017 [5] What Is Phishing Scam, https://usa.kaspersky.com/resourcecenter/ threats/spam-phishing last, 2020. [6] ”What is spyware? And how to remove it,” [Online], Available: https://goo.gl/rnXgfp, Accessed: 25 Apr 2019, Nov 2018 [7] D. He, S. Chan, and M. Guizani, “Mobile application security: malware threats and defenses,” IEEE Wireless Communications, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 138–144, 2015. [8] H. Hawilo et al., “NFV: State of the Art, Challenges and Implementation in Next Generation Mobile Networks (vEPC),” IEEE Network, vol. 28, no. 6, Nov./Dec.2014, pp. 18–26. [9] S. Intellect, ”What is a trojan downloader?,” [Online], Available: https://bit.ly/2vBlNo3, Accessed: 2 Apr 2019, 2018 [10] G. Tinari, ”Cult of android - your phone could be slower due to hidden ads,” [Online], Available: https://www.cultofandroid.com/74838/hidden-ads/, Accessed: 4 Apr 2019, July 2015 [11] A. O’Donnell, ”How to protect yourself from premium sms text message scams,” [Online], Available: https://goo.gl/7sCZ59, Accessed: 14 Apr 2019, March 2017 Review of Literature [1] N. Leavitt, \"Mobile security: Finally a serious problem,\" Computer, vol. 6, no. 44, pp. 10-15, 2011. [2] K. Marko, \"Rise of android botnets.,\" Informationweek - Online, 2011. [3] \"More mobile security glitches,\" Computer Fraud & Security, no. 7, p. 3-4 , 2011. [4] Khan, J., Abbas, H., & Al-Muhtadi, J. (2015). Survey on Mobile User\'s Data Privacy Threats and Defense Mechanisms. Procedia Computer Science, 56, 376- 383. [5] Cifuentes, Y., Beltrán, L., & Ramírez, L. (2015, August). Analysis of Security Vulnerabilities for Mobile Health Applications. In 2015 Seventh International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (ICMCN 2015). [6] Chatzikonstantinou, A., Ntantogian, C., Karopoulos, G., & Xenakis, C. (2016, May). Evaluation of Cryptography Usage in Android Applications. In proceedings of the 9th EAI International Conference on Bio-inspired Information and Communications Technologies, pp. 84-91. [7] Shukla, V., Chaturvedi, A., & Srivastava, N. (2015). A new secure authenticated key agreement scheme for wireless (mobile) communication in an HER system using cryptography. Communication on applied electronics (CAE), 3(3), pp. 17-22. [8] Choo, K. K. R. (2014). Mobile cloud storage users. IEEE Cloud Computing, 1(3), 20-23. [9] Agasi, O. (2015). Encapsulating mobile security. Computer Fraud & Security, 2015(6), 10-12. [10] Cheng, J., Wong, S. H., Yang, H., & Lu, S. (2007)“Smart-siren: virus detection and alert for smart-phones”, In Proceedings of the 5th international conference on Mobile systems, applications and services, pp. 256-61.
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Rakesh Kumar. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET63726
Publish Date : 2024-07-22
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

